Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM), often referred to as spark machining or spark erosion, is a revolutionary manufacturing technique that has transformed the way industries approach precision machining. Unlike conventional methods that rely on mechanical force to cut materials, EDM employs controlled electrical discharges to erode material from a workpiece. This non-contact machining process excels in creating intricate geometries, fine details, and smooth finishes, making it indispensable for applications requiring high precision.
Widely used in aerospace, automotive, medical, and tool-making industries, EDM enables the machining of hard and heat-resistant materials like titanium, tungsten, and carbide that are challenging to process using traditional techniques. From crafting intricate molds to producing tiny medical implants, EDM has proven to be a versatile and reliable technology.
In this blog, we will explore the working principles, types, applications, advantages, and challenges of EDM, shedding light on why it continues to play a pivotal role in modern manufacturing.
What is Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)?

Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a non-traditional manufacturing process used to shape and cut hard, electrically conductive materials by means of controlled electrical discharges, or sparks. Unlike conventional machining, which uses physical tools to cut or grind material, EDM relies on the principle of spark erosion, where high-frequency electrical sparks generate intense heat to remove material from the workpiece.
This process is particularly valuable for producing complex shapes, fine details, and precision components, especially in materials that are difficult to machine using traditional methods, such as hardened steel, titanium, tungsten, and carbide.
Key Features of EDM
- Contactless Machining: The tool and the workpiece never physically touch, reducing mechanical stresses and wear.
- Machining of Hard Materials: It can easily cut through tough and heat-resistant metals.
- Precision: EDM achieves tolerances as fine as ±0.005 mm and produces smooth, burr-free surfaces.
- Complex Shapes: Capable of creating intricate geometries, deep cavities, and sharp internal corners.
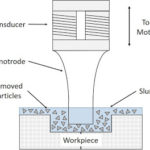
Main Components of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
The efficiency and precision of EDM depend on the combined effect between its key components. Below is a detailed explanation of the main components of an EDM system:
1. Workpiece
- Description: The material that is being machined.
- Requirement: The workpiece must be electrically conductive to allow the passage of electrical discharges.
- Common Materials: Hardened steel, Titanium, Tungsten carbide, Aluminum alloys
- Function: The workpiece interacts with the tool electrode to form the desired shape through spark erosion.
2. Tool Electrode (Electrode)
- Description: The electrode acts as the cutting tool and defines the final shape or geometry imparted to the workpiece.
- Material: Commonly made of copper, graphite, tungsten, or copper-tungsten alloys.
- Function:
- Transfers electrical energy to the workpiece.
- Acts as a template for the machined shape (in the case of Sinker EDM).
- In Wire EDM, the electrode is a thin wire that moves to cut the workpiece.
3. Dielectric Fluid
- Description: An insulating liquid medium (such as deionized water or oil) that fills the gap between the tool electrode and the workpiece.
- Functions:
- Insulates until the breakdown voltage is reached, allowing controlled spark generation.
- Flushes away debris (eroded material) from the machining zone.
- Cools the electrode and workpiece to prevent overheating.
- Helps in maintaining the stability of the spark discharge process.
4. Power Supply Unit
- Description: Provides high-frequency electrical pulses to the tool and workpiece.
- Functions:
- Generates the voltage and current needed to produce sparks.
- Controls the frequency and duration of electrical discharges.
- Regulates the energy levels to ensure precision and prevent damage to the workpiece.
5. Servo Mechanism
- Description: A system that controls the movement of the tool electrode and maintains the spark gap (the distance between the electrode and the workpiece).
- Functions:
- Automatically adjusts the electrode position to maintain an optimal spark gap.
- Enhances machining precision and efficiency by stabilizing the process.
6. Spark Gap
- Description: The tiny gap (typically 0.01–0.5 mm) between the tool electrode and the workpiece where the spark is generated.
- Importance:
- Determines the quality and precision of the machining process.
- Must be consistently maintained for effective material removal.
7. EDM Machine Base/Frame
- Description: Provides structural support for the entire system, including the workpiece, electrode, and machining head.
- Function:
- Ensures stability and vibration-free operation during machining.
8. Control Unit (CNC or Manual)
- Description: A system that manages the EDM process, either manually or through computerized control (CNC).
- Functions:
- Programs the machining path, spark parameters, and other settings.
- Allows for automation and precise repeatability in machining operations.
9. Filtration System
- Description: A system to filter the dielectric fluid.
- Function:
- Removes debris and contaminants to ensure consistent machining performance.
- Prolongs the life of the dielectric fluid and improves surface finish quality.
10. Workpiece Fixture
- Description: A mechanism to securely hold the workpiece in place during machining.
- Function:
- Prevents movement or vibration of the workpiece, ensuring precise machining.
Working of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)

Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) operates on the principle of controlled spark erosion to remove material from a workpiece. It is a non-contact process where high-frequency electrical discharges generate intense heat to vaporize or melt material. This method is ideal for machining hard and complex geometries that are difficult to achieve with conventional tools.
Here’s a step-by-step breakdown of how EDM works:
1. Setup and Preparation
- Workpiece and Tool Electrode:
- The workpiece is mounted on a machine bed and connected to a power source as one electrode.
- The tool electrode, made of materials like graphite or copper, is also connected to the power supply.
- Both electrodes are submerged in a dielectric fluid (such as deionized water or hydrocarbon oil).
- Gap Maintenance:
- A small, controlled gap (known as the spark gap) is maintained between the tool and the workpiece.
- This gap is critical to generating consistent electrical discharges.
2. Application of Voltage
- A high-frequency electrical pulse is applied between the workpiece and the tool electrode.
- The dielectric fluid initially acts as an insulator, preventing current flow.
3. Spark Generation
- When the voltage exceeds the breakdown strength of the dielectric fluid, it ionizes, creating a conductive plasma channel.
- This ionization allows a spark to jump across the gap between the tool and the workpiece.
4. Material Removal
- The spark generates intense heat (8,000°C to 12,000°C) in a localized area.
- This heat melts or vaporizes a tiny portion of material from both the workpiece and the tool.
- The molten material forms microscopic craters on the workpiece.
5. Cooling and Debris Removal
- The dielectric fluid plays a vital role in flushing away eroded particles (debris) from the machining zone.
- It also cools the workpiece and the electrode, preventing overheating and thermal damage.
6. Repetition
- The spark generation and material removal process repeat thousands of times per second.
- This rapid and continuous erosion shapes the workpiece into the desired geometry, layer by layer.
7. Controlled Movement
- Servo Mechanism:
- A servo control system adjusts the tool electrode’s position to maintain the optimal spark gap.
- CNC Programming (if applicable):
- In modern EDM machines, CNC systems control the path and depth of the electrode with high precision, enabling intricate designs.
8. Surface Finishing
- The process naturally leaves a smooth and burr-free surface.
- The surface quality depends on the spark frequency and energy settings. Higher frequencies produce finer finishes, while lower frequencies are used for faster material removal.
Types of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
EDM technology has evolved to meet diverse machining needs, leading to different types of EDM processes. Each type specializes in specific applications and operates on the same principle of spark erosion but varies in execution and tooling. Below are the main types of EDM:
1. Die-Sinking EDM (Sinker EDM)
Overview
Sinker EDM, also known as Ram EDM, uses a shaped electrode to create complex cavities and contours in the workpiece. The electrode is typically made of materials like graphite or copper and is machined to mirror the desired shape.
How It Works
- The electrode and workpiece are submerged in a dielectric fluid.
- Controlled electrical discharges occur between the tool and the workpiece.
- The material is eroded layer by layer to match the shape of the electrode.
Applications
- Mold and die making.
- Manufacturing complex parts like cavities, gears, and turbine blades.
Advantages
- Creates intricate shapes and deep cavities.
- Produces fine surface finishes.
- Handles hard materials with ease.
2. Wire EDM (Wire-Cut EDM)
Overview
Wire EDM uses a thin, continuously fed wire as the cutting tool to slice through the workpiece. The wire is usually made of brass or copper and does not make physical contact with the workpiece.
How It Works
- The wire and workpiece are immersed in a dielectric fluid, often deionized water.
- Electrical discharges occur between the wire and the workpiece, eroding material along a programmed path.
- The wire is constantly renewed to maintain cutting efficiency.
Applications
- Cutting intricate profiles, contours, and geometries.
- Creating extrusion dies, punches, and precision parts.
Advantages
- Can cut complex shapes with tight tolerances.
- No tool wear since the wire is constantly replaced.
- Ideal for machining very thin sections.
3. Hole-Drilling EDM
Overview
This type of EDM is specialized for drilling small, precise holes in hard materials that are difficult to machine with conventional drills.
How It Works
- A tubular electrode rotates and discharges sparks to drill holes.
- The dielectric fluid flushes debris from the machining zone.
Applications
- Creating cooling holes in turbine blades.
- Drilling fine holes in medical and electronic components.
Advantages
- Can drill extremely small and deep holes.
- Handles hard and brittle materials.
- Produces holes with high aspect ratios.
4. Dry EDM
Overview
Dry EDM uses a gaseous dielectric medium (like air or gas) instead of liquid dielectric fluid.
How It Works
- Electrical discharges occur in a pressurized gas environment.
- The gas acts as an insulating medium and assists in debris removal.
Applications
- Environmentally sensitive applications where liquid dielectric is not suitable.
- Machining delicate or thin materials.
Advantages
- Eco-friendly as it eliminates the need for liquid dielectric.
- Reduces thermal damage to the workpiece.
5. EDM Milling
Overview
A newer approach, EDM milling uses a rotating electrode to machine the workpiece, similar to conventional milling but with spark erosion.
How It Works
- The rotating electrode shapes the workpiece through controlled sparks.
- Ideal for machining complex geometries.
Applications
- Creating intricate 3D shapes.
- Milling in hard materials like carbide.
Advantages
- Combines the versatility of milling with EDM precision.
- Enables multi-axis machining.
6. Rotary EDM
Overview
Rotary EDM uses a rotating electrode, typically tubular, to machine circular features like holes or contours.
How It Works
- Sparks erode material while the electrode rotates.
- Provides a uniform finish and precise circular geometries.
Applications
- Machining nozzles, circular grooves, and complex contours.
Advantages
- Improves surface finish and precision.
- Efficient for machining cylindrical features.
Comparison of EDM Types
| Type | Tool/Electrode | Applications | Key Features |
|---|---|---|---|
| Sinker EDM | Shaped electrode | Molds, cavities, gears | Deep cavities, intricate shapes |
| Wire EDM | Thin wire | Dies, precision profiles | No tool wear, fine tolerances |
| Hole-Drilling EDM | Tubular electrode | Cooling holes, medical parts | Small, deep holes with high aspect ratios |
| Dry EDM | Gaseous dielectric | Thin materials, eco-sensitive | Eco-friendly, reduced thermal damage |
| EDM Milling | Rotating electrode | 3D geometries, hard materials | Combines milling and EDM |
| Rotary EDM | Rotating tubular electrode | Nozzles, circular grooves | Uniform finish, precise round shapes |
Advantages of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a versatile and highly effective machining process, especially for hard-to-machine materials and complex geometries. Below are the primary advantages of EDM:
1. Precision and Accuracy
- EDM offers exceptional precision with tolerances as fine as ±0.005 mm.
- Ideal for creating intricate details, sharp corners, and fine features that are difficult or impossible with conventional machining.
- It produces components with smooth and burr-free surfaces.
2. Ability to Machine Hard Materials
- EDM can machine extremely hard and tough materials, including titanium, tungsten carbide, hardened steel, and Inconel.
- It is widely used in industries requiring high-strength components, such as aerospace, automotive, and medical sectors.
3. Non-Contact Process
- The tool electrode and workpiece never physically touch, which eliminates mechanical stresses and tool pressure on the material.
- This feature is particularly beneficial for machining delicate or thin parts.
4. Complex Geometries
- EDM can create intricate shapes, deep cavities, and thin-walled sections with high accuracy.
- It is ideal for components requiring complex 3D geometries, such as molds, dies, and turbine blades.
5. Burr-Free Machining
- EDM leaves no burrs or sharp edges on the workpiece, eliminating the need for secondary finishing operations.
- This results in smoother surfaces and reduced post-processing time.
6. Capability to Drill Small and Deep Holes
- EDM can produce small-diameter holes with high aspect ratios (depth-to-diameter ratio).
- It is often used to create cooling holes in turbine blades and precise holes in medical devices.
7. Versatility with Material Conductivity
- As long as the workpiece is electrically conductive, EDM can machine any material, regardless of its hardness or brittleness.
- Materials like ceramics with conductive coatings can also be machined.
8. High Surface Finish Quality
- EDM provides excellent surface finishes, with roughness values as low as Ra 0.1 µm, depending on process parameters.
- This makes it suitable for applications requiring high aesthetic and functional standards, such as molds and dies.
9. No Tool Wear
- In Wire EDM, the tool (wire) is constantly renewed, ensuring consistent cutting performance.
- In Die-Sinker EDM, the wear on the electrode is minimal due to controlled spark erosion.
10. Minimal Operator Skill Required
- CNC-controlled EDM machines automate much of the machining process.
- Operators can rely on pre-programmed instructions, reducing dependency on manual expertise.
11. Environmentally Friendly Options
- Dry EDM, which uses gaseous dielectrics instead of liquid ones, is an eco-friendly alternative that reduces fluid disposal issues.
12. Minimal Distortion
- Since EDM involves no cutting forces and operates at low temperatures, it minimizes thermal and mechanical stresses on the workpiece.
- This ensures dimensional stability and reduces the risk of deformation.
13. Compatibility with Fragile Parts
- EDM is suitable for machining thin, fragile, or heat-sensitive materials without causing damage, as the process is non-contact and precisely controlled.
14. Automation and Efficiency
- Modern EDM systems are equipped with automation features like multi-axis CNC control, automatic wire threading, and adaptive machining, which enhance productivity.
- EDM machines can run unattended for extended periods, improving operational efficiency.
Applications of Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM)
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is widely used across various industries due to its ability to machine complex geometries, hard materials, and intricate designs with high precision. Below are the key applications of EDM:
1. Aerospace Industry
EDM is extensively used in aerospace applications where precision and material toughness are critical.
- Turbine Components: EDM is used to create intricate cooling holes in turbine blades and vanes.
- Fuel System Parts: Manufacturing fuel injector nozzles with micro-sized features.
- Exotic Materials: Machining superalloys like Inconel, titanium, and tungsten carbide for engine components.
- Lightweight Structures: Creating complex shapes in lightweight and heat-resistant materials.
2. Automotive Industry
The automotive sector relies on EDM for producing components with tight tolerances and intricate designs.
- Molds and Dies: Manufacturing molds for plastic injection molding and metal stamping dies.
- Gears and Transmission Parts: Producing high-precision gears, splines, and transmission components.
- Prototyping: Creating prototype parts for vehicle development and testing.
- Engine Components: Machining components like cylinder heads, valves, and pistons.
3. Tool and Die Making
EDM is a cornerstone of the tool and die industry, thanks to its precision and ability to machine hard materials.
- Injection Molds: Used to create molds with detailed surface textures and intricate shapes.
- Punches and Dies: Fabricating high-durability punches and dies for stamping and forging.
- Fine Details: Crafting sharp internal corners and intricate details in die sets.
4. Medical and Dental Industry
EDM plays a crucial role in the production of medical devices and surgical tools.
- Surgical Instruments: Manufacturing precision instruments like scalpels, forceps, and scissors.
- Medical Implants: Creating orthopedic implants, such as knee and hip joints, with high accuracy.
- Micro-Machining: Producing tiny and precise parts for dental devices and minimally invasive surgical tools.
5. Electronics Industry
The demand for miniaturized components in electronics makes EDM indispensable.
- Micro-Connectors: Fabricating connectors and terminals with high precision.
- Semiconductor Tools: Producing molds and tools for semiconductor packaging.
- Micro-Holes: Drilling fine holes in components like circuit boards.
6. Mold Making
EDM is extensively used to create molds for a variety of applications.
- Plastic Injection Molding: Producing molds for consumer products, automotive parts, and industrial equipment.
- Die-Casting Molds: Crafting molds for casting metals like aluminum and zinc.
- Textured Surfaces: Creating intricate surface textures on molds for aesthetic and functional purposes.
7. Precision Engineering
In industries where accuracy is critical, EDM offers unmatched precision.
- Watchmaking: Creating miniature components for luxury and precision watches.
- Optics: Machining molds for lenses and other optical components.
- Micromechanics: Producing parts for micro-machines and robotics.
8. Energy Sector
EDM is vital in the production of components for power generation systems.
- Gas Turbines: Creating cooling channels and intricate parts for turbines.
- Nuclear Industry: Machining components for reactors, including nozzles and control rods.
- Renewable Energy: Manufacturing precision parts for wind and solar energy equipment.
9. Prototyping and R&D
EDM is frequently used in research and development for creating prototypes and testing designs.
- Rapid Prototyping: Quickly producing parts for design validation.
- Material Testing: Machining hard-to-work materials for experimental purposes.
10. Jewelry Industry
EDM is used to craft intricate designs and shapes in precious metals.
- Fine Detailing: Creating elaborate patterns in gold, silver, and platinum.
- Custom Designs: Machining bespoke jewelry pieces with precision.
11. Defense and Military
The defense sector utilizes EDM for high-performance components and specialized applications.
- Weaponry: Manufacturing precision parts for firearms and ammunition.
- Aerospace Defense: Crafting components for military aircraft and missiles.
- Durable Materials: Machining parts from hard and heat-resistant materials for durability.
12. Additive Manufacturing (Support)
EDM complements additive manufacturing processes by providing post-processing capabilities.
- Finishing: Refining parts made by 3D printing.
- High Precision: Adjusting features and tolerances on complex shapes.
Conclusion
Electrical Discharge Machining (EDM) is a cutting-edge process that excels in precision, complexity, and the ability to machine hard materials. Its versatility, from Wire EDM to Sinker EDM, makes it indispensable in industries like aerospace, automotive, and medical. Despite its reliance on conductive materials, EDM’s non-contact nature, accuracy, and superior surface finish ensure it remains a vital tool in modern manufacturing, meeting the demands of advanced engineering with reliability and efficiency.
Explore More:
- What is Plasma Arc Machining (PAM) And How it Works?
- Laser Beam Machining – Main Parts, Principle, Working with Application
- Water Jet Machining – Working Principle, Advantages and Disadvantages with Application
- Ultrasonic Machining (USM) – Main Parts, Working Principle, Advantages and Disadvantages with Application