In mechanical engineering, boilers play a vital role in converting thermal energy into usable mechanical power, and among the classical designs, the locomotive boiler holds a special historical and academic importance. Widely used in railway steam engines and early marine applications, the locomotive boiler is known for its compact construction, mobility, and high steam generation capacity.
A locomotive boiler is a horizontal, multi-tubular fire tube boiler that operates on natural circulation and uses artificial draft created by exhaust steam. It is specifically designed to meet sudden and fluctuating steam demands, which makes it suitable for mobile applications like railways. Due to its simple design and efficient heat transfer mechanism, it remains a core topic in mechanical engineering curricula, competitive exams, and technical interviews across the globe.
In this detailed guide, you will learn what a locomotive boiler is, its construction and main parts, working principle, along with its advantages, disadvantages, applications, FAQs, and an interactive knowledge quiz. This explanation is structured in a student-friendly and exam-oriented manner, making it useful for diploma, undergraduate, and competitive exam aspirants.
Construction or Main Parts
The construction or main parts of a locomotive boiler are:
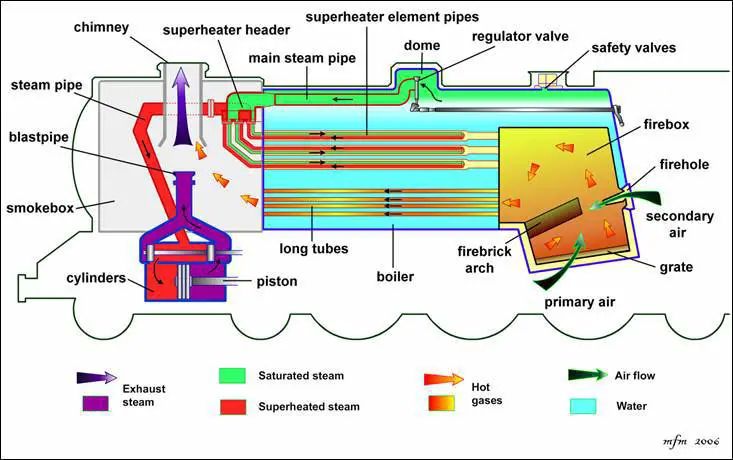
1. Fire hole:
It is a hole provided at the rear end of the boiler. The solid fuel is inserted and ignited into the furnace through this hole.
2. Fire box:
It is a box in which the burning of the fuel takes place.
3. Grate:
Grate is a platform on which the solid fuel is kept and burnt.
4. Fire Brick Arch:
It is a brick arch placed inclined over the grate. It prevents the entry of the ash, dust and burnt fuel particles into the fire tubes. It provides a way to the hot flue gases to travel a definite path before entering into the fire tubes of the boiler.
5. Boiler Tubes:
They are the fire tubes through which the hot flue gases pass and exchange the heat with the surrounding water.
6. Smoke Box:
According to its name, it is a box in which the smoke of the burnt fuel after passing through the fire tubes gets collected. From there it is exhausted in the environment by the chimney.
7. Blast Pipe:
It is a pipe provided above the steam engine. The exhaust steam passes through this blast pipe. It is used to create an artificial draft that pushes the smoke out through the chimney and creates suction for the hot flue gases. The suction created allows the hot flue gases to move forward through the fire tubes.
8. Steam Pipe:
It is a pipe through which the steam passes. We have two steam pipes; one is the main steam pipe present in between the superheater header and dome. And the second one is that which connects the superheater exit end to the steam engine.
9. Superheater:
It superheats the steam to the desired temperature before entering into the cylinder of the steam engine.
10. Super Heater Element Pipes:
These are the pipes of superheater through which the steam travels and gets superheated.
11. Dome:
It is present at the top and contains the regulator for regulating the steam produced through the steam pipe.
12. Regulator valve:
It is a valve that regulates the steam through the main steam pipe for superheating.
13. Safety Valve:
It is used to maintain the safe working steam pressure in the locomotive boiler. It blows off steam when the pressure of the steam increases above safety level and prevents blasting of the boiler.
14. Superheater Header:
It is the head of the superheater which accepts the steam from the steam pipe.
15. Chimney:
It is used to throw out the exhaust smoke and gases to the environment. The length of the chimney is very small in this boiler.
Also Read:
- Lamont Boiler – Main Parts, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Cochran Boiler – Main Parts, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages
- Lancashire Boiler Construction, Working with Diagram
Working of Locomotive Boiler
- In the locomotive boiler, first, the solid fuel (coal) is inserted on the grate and is ignited from the fire hole. The burning of the fuel starts and it creates hot flue gases. A fire brick arch is provided that makes the flow of hot flue gases to a definite path before entering into the long tubes (fire tubes). It also prevents the entry of burnt solid fuel particles into the fire tubes.
- The hot flue gases pass through the long fire tubes and heat the water surrounding them. Due to the heating, the water gets converted into saturated steam and gets collected at the top.
- The saturated steam from the dome enters into the main steam pipe through the regulator valve. The steam travels in the main steam pipe and reaches to the superheater header. Form header, the steam enters into superheater element pipes. Here it is superheated and then the superheated steam enters into the steam pipe of the smoke box.
- The steam from the superheater goes to the cylinder containing piston. The superheated steam made the piston moves within the cylinder. The piston is connected to the wheels of the steam engine and the wheels start rotating.
- The exhaust steam from the cylinder enters into the blast pipe. The burnt gases and smoke after passing through the fire tubes enter into the smokebox. The exhaust steam coming out from the blast pipe pushes the smoke out of the boiler through the chimney. Here the smoke cannot escape out from the boiler on its own, so artificial draft is created by exhaust steam coming out from the steam engine. This artificial draft created pushes the smoke out of the smokebox and creates suction for the hot flue gases.
For a better explanation of the working of locomotive boiler watch the video:
Also Read:
- Lever Safety Valve – Definition, Main parts and Working
- Steam Condenser – Definition, Working, Types and Advantages
- Benson Boiler – Construction, Working Principle and Advantages
Advantages of Locomotive Boiler
- It is portable and can be easily transported.
- It is capable of meeting sudden and fluctuating demands of steam.
- It is a cost-effective boiler.
- It has a high steam generation rate.
- It is compact in size and its operation is easy.
Disadvantages
- It faces the problems of corrosion and scale formation.
- Unable to work under heavy load conditions because of overheating problems.
- Some of its water spaces are difficult to clean.
Application
Locomotive boilers are mostly used in railways and marines. The efficiency of this boiler is very less. It cannot work in heavy-load conditions because this leads to the overheating of the boiler and finally gets damage. They are also used in traction engines, steam rollers, portable steam engines, and some other steam road vehicles.
Conclusion
The locomotive boiler represents an important milestone in the evolution of steam power technology and continues to be a foundational study topic in mechanical engineering. Although it is largely replaced by modern high-efficiency boilers in practical applications, understanding its construction, working principle, and operating characteristics is essential for building strong conceptual knowledge.
FAQs
A locomotive boiler is a horizontal, multi-tubular, fire tube boiler used in railway steam engines to generate steam at a high rate. It is a mobile boiler fired by solid fuel.
A locomotive boiler is a fire tube boiler, where hot flue gases flow through tubes and water surrounds the tubes.
It is called a mobile boiler because it is mounted on a locomotive engine and moves along with the train, unlike stationary boilers.
A locomotive boiler uses solid fuel (coal), which is burned on the grate inside the firebox.
The blast pipe creates an artificial draft by using exhaust steam, helping to remove smoke through the chimney and draw hot gases through fire tubes.
The fire brick arch:
– Directs hot gases along a fixed path
– Prevents ash from entering fire tubes
– Improves combustion efficiency
A locomotive boiler operates at medium steam pressure compared to modern high-pressure boilers.
Main advantages include:
– High steam generation rate
– Compact and portable design
– Quick response to load changes
– Simple operation
Major disadvantages are:
– Low thermal efficiency
– Corrosion and scale formation
– Difficulty in cleaning
– Not suitable for heavy load conditions
Locomotive boilers are used in:
– Railway steam engines
– Marine applications
– Traction engines
– Steam rollers and portable steam engines
Locomotive Boiler – Knowledge Check
⚠️ Please select an option before continuing.






Thanks for sharing such a nice info with us. I appreciate this blog regarding Locomotive Boiler.