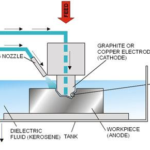
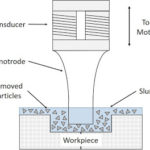
In aerospace manufacturing, insufficient precision in gear machining leads to component failures and cost overruns, often due to outdated methods and inadequate quality control. This article outlines strategies to enhance accuracy by integrating CNC Machining and optimizing the gear generating process, adhering to strict engineering standards for improved efficiency.
What are the Core Challenges of the Gear Generating Process?
The gear generating process is a fundamental manufacturing technique where the tooth form is progressively created through the relative motion between a cutting tool and the gear blank. Understanding how to make gears using methods like hobbing and shaping is essential for addressing the inherent challenges of this process, which include achieving precision and minimizing material waste.
Accuracy and Consistency Deficits
The primary objective in gear manufacturing is to achieve micron-level geometric accuracy and perfect consistency across production batches. However, traditional techniques often fall short in this regard.
- Controlling Complex Tooth Forms
For complex profiles commonly used in aerospace, such as involute and arc tooth forms, controlling profile and lead errors is exceptionally challenging. Even minor deviations can result in increased meshing noise, vibration, and a loss of transmission efficiency, underscoring the need for precise geometric definition as highlighted in standards like those from the American Society of Mechanical Engineers (ASME).
- Material and Heat Treatment Distortion
High-performance gears made from high-strength alloy steels are susceptible to distortion during quenching processes. This distortion can compromise the precision achieved during initial machining, often necessitating secondary finishing operations like grinding to correct the errors, which adds time and cost.
Efficiency and Cost Constraints
Beyond precision, the economic viability of the manufacturing process is crucial. Traditional gear generation often relies on dedicated machinery and skilled operators, leading to lengthy setup times and slow changeovers.
Furthermore, significant material waste can occur during rough machining to allow for subsequent finishing operations, increasing raw material costs. These challenges highlight the need for a more flexible and precise manufacturing approach, naturally leading to the application of modern CNC Machining technologies.
How Does CNC Machining Optimize Gear Manufacturing Efficiency?
The introduction of CNC Machining has revolutionized gear manufacturing, bringing unprecedented levels of automation and precision to the entire production workflow. This technology has significantly advanced Manufacturing Processes by executing digital instructions with exceptional consistency.
Compared to dedicated machines that rely on mechanical cams and templates, CNC machines offer distinct advantages. They effortlessly achieve micron-level repeatability, ensuring each gear tooth adheres strictly to the digital model’s specifications and drastically reducing human error.
The application of CNC Machining is particularly valuable for producing complex components like turbine blades and structural parts, where tight tolerances are mission-critical. For those seeking a deeper understanding of this synergistic application, a detailed Gear Generating Guide is available.
What Role Does Engineering Design Play in Gear Generation?
Superior manufacturing begins with superior design. In the realms of gear generating and gear forming, engineering design is the decisive factor influencing the final product’s performance, reliability, and manufacturability. This is especially critical in demanding fields like automotive engineering and aerospace.
During gear design, engineers define key parameters and select materials like case-hardening steels or composites based on operational requirements . Geometric optimization techniques, such as profile modification, are used to enhance performance and durability . Simulation-based verification and Design for Manufacturability (DFM) collaboration with manufacturing teams are critical best practices to prevent costly errors and ensure precision .
How to Ensure Quality Control for Aerospace Gears?
For flight-safety-critical Aerospace Components, quality control is not merely a final inspection step but an integrated system spanning the entire production process, from raw material inspection to final shipment. In gear manufacturing, this entails rigorous inspection standards and certification requirements.
The core of quality control lies in verification. This involves using coordinate measuring machines (CMM) or specialized gear testers to conduct 100% inspection or high-frequency sampling of key parameters like tooth profile, lead, and pitch to ensure full compliance with design specifications. For the most critical applications, gear grinding services are often employed as the final finishing step, after which surface roughness and residual stress are also meticulously inspected.
International standards form the foundation of quality. The aerospace industry’s adherence to the AS9100D quality management system provides a framework for these rigorous requirements. The implementation of automated systems, including robotic arms with vision systems and laser scanners, enables precise measurement of intricate features, ensuring every part meets exact design specifications. This level of quality assurance often relies on partners with profound expertise and strict process controls, making the selection of professional Gear machining services crucial.
Also Read:
- Water Jet Machining – Working Principle, Advantages and Disadvantages with Application
- Advantages of Electron Beam Machining
- What is CNC Machine – Main Parts, Working, Block Diagram
What are the Best Practices for Custom Spiral Bevel Gear Generating Services?
Addressing the needs of high-end sectors like aerospace and specialized vehicles, custom spiral bevel gear generating services provide essential solutions. The successful delivery of these custom services is guided by a set of established best practices.
Collaborative Design and Engineering Analysis
Best practices start with deep collaboration between the customer and the engineering team. Service providers should conduct thorough load analysis and simulation based on the application’s specific conditions (torque, speed, installation space) to optimize the gear’s local contact pattern (LTCA). This ensures optimal performance under real-world loads, moving beyond simply meeting drawing dimensions to avoid performance risks hidden by “to-print” manufacturing.
Integrated Process Planning
The entire workflow, from blank forging and heat treatment to gear generating and final grinding, requires meticulous planning.
- Advanced Machining and Generating Technologies
Beyond employing 5-axis CNC machining for high-precision milling or using specialized equipment like Gleason machines, the process must carefully plan the allocation of machining allowances before and after heat treatment. It also involves integrating advanced gear grinding services or hard turning for final finishing to simultaneously ensure surface hardness, precision, and integrity.
- Predictive Production and Smart Scheduling
Utilizing digital systems to simulate and optimize the production flow allows for accurate bottleneck prediction. Intelligent scheduling helps balance resources, which is key to reducing lead times for custom parts. For example, grouping batches with similar processes can minimize machine setup times.
Closed-Loop Quality and Data Feedback
Establishing a dedicated “digital quality file” for each custom gear, recording everything from material certificates to inspection data for each operation, is vital. This data not only serves for final validation but also provides feedback to design and process engineering departments, enabling continuous optimization of algorithms and parameters. This creates a closed-loop system of “design-manufacture-inspect-optimize,” steadily improving the success rate and efficiency of future custom projects.
Conclusion
This article has systematically analyzed the industry-wide challenge of insufficient gear precision and explored a comprehensive strategy involving the optimization of the gear generating process, deep integration of CNC Machining technology, strengthened upfront collaboration in engineering design, and the implementation of end-to-end quality control systems. This integrated approach is key to enhancing gear accuracy and reliability, while also controlling overall costs and shortening project cycles.
Readers facing challenges in manufacturing high-precision gears or seeking more efficient solutions for their projects are encouraged to research relevant engineering standards and best practices. Engaging with experienced and fully qualified service providers can help apply the strategies discussed herein to achieve both performance and economic goals.
Author Biography
This article was authored by a seasoned expert in the field of precision manufacturing, with knowledge derived from decades of practice in high-precision component manufacturing. The expert’s company, JS Precision, adheres to the highest industry standards, holding internationally recognized quality management system certifications such as ISO 9001, IATF 16949, and AS9100D, ensuring every step from design to delivery meets rigorous professional requirements.
FAQs
A: Gear generation is a manufacturing process where the tooth form is created by the relative motion between a cutting tool and a gear blank. It involves methods like hobbing and shaping, which enhance efficiency and reduce material waste, making it suitable for high-precision applications in aerospace and automotive industries.
A: CNC technology utilizes computer control to automate the machining process, ensuring tolerances within micron levels. It minimizes human error and optimizes the gear generating process, thereby improving overall quality, reducing costs, and enabling the manufacture of complex geometries.
A: Gear grinding services provide superior surface finish and precise tolerances, which extend the component’s operational life. By removing material excess, they enhance performance in high-load applications like automotive transmissions, reducing noise and increasing reliability.
A: Material selection depends on load capacity, operating environment, and temperature. Common choices include steel and composites. Engineering design analysis helps optimize performance and prevent failure, guided by international standards like ISO for compatibility.
A: Lead time varies with complexity and order volume, typically ranging from weeks to months. Optimized manufacturing processes and robust quality control can shorten this cycle. Advance planning and clear communication with suppliers are recommended to avoid delays.