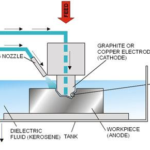
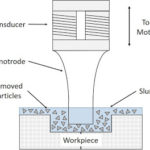
If you’ve ever been curious about the term CNC machine, you’re not alone. This acronym is widely used in manufacturing and engineering industries. In this blog, we’ll uncover the full form of CNC, delve into its significance, and explore how these machines have revolutionized modern manufacturing.
What is the Full Form of CNC?
CNC stands for Computer Numerical Control. It refers to a system where a computer is used to control machining tools such as drills, lathes, and mills. The process enables precision, automation, and efficiency in manufacturing operations.
How CNC Machines Work?
CNC machines operate using pre-programmed software that dictates the movement of tools and machinery. Here’s how the process works:
- Design Stage: Engineers create a CAD (Computer-Aided Design) model of the part to be manufactured.
- Programming Stage: The CAD model is converted into G-code, a programming language that CNC machines can interpret.
- Machine Operation: The CNC machine executes the G-code instructions to cut, shape, or drill the material as required.
Types of CNC Machines
CNC technology can be applied to various machines. Here are some common types:
- CNC Milling Machines: Used for cutting and shaping solid materials.
- CNC Lathes: Ideal for creating cylindrical parts.
- CNC Plasma Cutters: Used for cutting metal using a plasma torch.
- CNC Laser Cutters: Precision tools for cutting and engraving materials like metal, plastic, and wood.
- CNC Grinders: Employed for grinding materials into desired shapes and sizes.
Advantages of CNC Machines
The advent of CNC machines has brought numerous benefits to manufacturing, including:
- High Precision: Accurate cutting and shaping reduce material wastage.
- Automation: Eliminates the need for manual intervention, saving time and labor costs.
- Consistency: Ensures uniformity in mass production.
- Versatility: Suitable for a wide range of materials and applications.
- Safety: Minimizes risks associated with manual machining processes.
Applications of CNC Machines
CNC machines are integral to industries like:
- Automotive: Manufacturing components like gears and engine parts.
- Aerospace: Creating high-precision parts for aircraft.
- Medical: Producing surgical instruments and prosthetics.
- Electronics: Crafting intricate circuit boards and enclosures.
- Furniture: Designing and shaping wood for custom furniture.
Future of CNC Machines
With advancements in technology, CNC machines are evolving to include features like:
- 5-Axis Machining: Enables more complex designs and intricate cuts.
- IoT Integration: Machines connected to the Internet of Things for real-time monitoring and efficiency.
- Artificial Intelligence: Enhanced decision-making and predictive maintenance capabilities.
Conclusion
The full form of CNC, Computer Numerical Control, represents a cornerstone of modern manufacturing. By combining precision, automation, and versatility, CNC machines have transformed industries across the globe. Whether you’re a student, an engineer, or just a curious mind, understanding CNC technology opens the door to the fascinating world of advanced manufacturing.

Author Bio
Pankaj Mishra is a Mechanical Engineer with 10+ years of experience in content creation. He simplifies complex engineering concepts into engaging and insightful content, empowering readers to learn and explore the world of technology.