Forging is a process, used for adapting the desired shape by the action of hammering or pressing. The materials that are used in this process are generally in the form of ingot, which is produced by the manufacturing companies for applying mechanical operations. Forging is a very old metal working technique, used for shaping. In the early days when there was truancy of advanced digital machines then manual forging operations were done. In those days firstly material being heated in coal furnace then put it on an anvil after that hand-hammering operation done on workpiece to give it a desired shape.
In the current, when machines become more brainy and are able to produce components ranging from a small nut to turbine rotor.

Forging operation is carried out by plastic deformation of the material in between two dies which cross over its mould design on the fed material. There are different type of die frame-up which is gonna use as concern of favourable shape. In the designing of simple product open die forging is adapted but if there is a need for a complex part to be forge, close die technique come into know. This die generally asked for molten metal as feeding material. In open die forging simple hammering operation carried out manually or by machines and shape configuration is obtained.
While working on a closed die, on squeezing the die the same shape which have been Digg on-die prints on the product, the extra material comes out from the die which is removed by the path of peripheral and being trimmed latter.
There are two main types of closed die forging come into know-
- Press forging
- Drop forging
In press forging material is squeezed between dies very slowly with the use of mechanical press or hydraulic press. Because of its slow operation the final product comes with more dimensional accuracy and fine surface area is received.
In drop forging one material is put into the die and hammering action continues on the die anvil until it takes desired shape. Wrenches, piston and crankshaft are typical example of automobile parts made under forging operation.
Example image
Operational Advantage
- Forging allows a huge range of products of the parts.
- It doesn’t requires any secondary operation i.e. the final product comes out from the die in a single process.
- Forging facilitates very less cost of production unless initial cost of dies are very high.
- The typical design can be achieved quickly.
- Forging products are very strong and reliable in comparison to other manufacturing
- Due to dimensional accuracy, machining and finishing option doesn’t requires, which reduces its cost of the product.
- High rate of production is obtained.
Disadvantage
- Limitations of the product size on accord to the press hammer.
- Drop forging makes a dangerous environment of manufacturing.
- For setting up the dies, initial cost is much higher.
- During operation high residual stress is produced.
- Because of more breaking chances, brittle material can not be forged.
Microstructure Effects
- In the forging process, well-defined grain orientation can be achieved.
- This operation elongates the grain structure in the direction of the deformation.
- Fibrous microstructure is obtained by the metal flow, allows better mechanical properties in the product.
- Due to workpiece undergoes recrystallization, it improves mechanical properties.
Orientation of Grain
In forging operation the object undergo completely change in its physical behaviour. The change in material shape starts from the grain boundary. It shows that redistribution of grain in working direction. On the other hand in casting operation technique the orientation of grains are epitaxial dendritic or Episcopal grains.
Also Read:
Types of Forging

In early days there were no machines available. The maximum operation was done manually which was time-consuming. But as days passed new inventions arises new machines. Except for manual process, forging process has been classified on behalf of-
- Equipment used-
- Drop forging
- Press forging
- By process –
- Open die forging
- Closed die forging
Drop forging –
In drop forging subject material is put into die then a weighted hammer is impacted continuously until it gains the desired shape as we required.
Press forging-
This contains slower operation than the drop forging. Here impact loading is not occurs in result of which more accurate dimension and the better surface finished object is obtained. There is only lag that it produces more residual stress during operation.
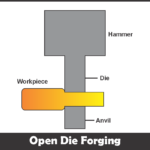
Open die forging-
In open die forging molten metal flow may be allowed. This is a hot mechanical forging operation between flat or shaped die.
The stock of material is placed on die anvil, then forging hammer jumped on it. Due to impact load, the stock of material present wear a shape which is present on die. Further this stock of material is being cold and comes out as finished goods.
Closed die forging-
It is clear by its name that it contains closed die set up. The hot workpiece being filled within the cavity of the die and after that die comes together to enclose the structure. Extra material comes out by its peripheral spaces. On cooling of the final object, there may be some minor irregularities which can be removed by ramming.
Die images
Coining Process
It is a type of closed die forging process in which pressure force is applied on the workpiece in a portion or entire surface is covered . In this process the workpiece is positioned to parallel to the dividing line of forging. Here the workpiece is subjected to high stress to induce plastic deformation in the respect of the die. This process results in very close tolerance, smoothed surface and eliminates the drafts.
Industrial applications-
- Minting of coins and medals
- Jewellery market
- Rare electric parts
- Making of badges and buttons
- Such kind of parts which one needs more polished surface.
Cogging Process
The cogging process is used to change the internal structure of the ingot. Ingots are the type of metal formed in rectangular or square shape by the process of moulding to perform other mechanical operation.
Cogging uses hot metal handling technique. Metal is being heated up to the malleable point but it should not be melted. This process allows using of a separated open and closed die.
Cogging process can be set up in a single action with the help of moment and rotation of the billet. There must be cooling arrangement as a blow to cool down the billet and rest at the bottom die.
Also Read:
- What is Casting Defects – Types, Causes and Remedies?
- 37 Types of Hammers that You Don’t Know?
- What is Annealing Process and Why it is done?
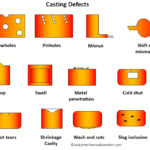
Defects in Forged Parts
There is no doubt that forging is one of the best manufacturing process that provides good mechanical strength used by industries.
Every process have some merits and demerits. Defects can be avoided by following their parameters. Major defects being seen due to irregularities in the surface of the die so there is a need for proper designing of the die. So during forging operation industry’s and workshops should take necessary measures in to know to avoid such kind of defects
Unfilled Section
Generally this kind of defect seen when molten metal is used in closed die forging.
Molten metal is filled in die but due to poor design of die, poor hearing is done and defined distribution of material is not occurs. Some unfilled points being remains which further comes out as a defect.
Cold Shuts
This defect occurs at the corners of the product in the form of small cracks. It also occurs due to improper design of the die. For prevention of this defect the fillet radius is needed to be increased.
Scale Pits
When proper finishing is not being done just after the operation the irregularities become very hard and it takes much more effort to remove. So to avoid this defect cleaning operation must be done quickly just during the forging operation.
Flakes
Flakes is caused due to undefined cooling arrangement. It results in internal cracking in the workpiece. When the product is cooled very quickly then sudden temperature loss occurs and product particles contracts due to contraction of grains, cracks occur. This crack directly affects the mechanical property of the product. Proper cooling can reduce the chances of this defect.
Undefined Grain Growth
When the metal had no proper rate of flow during the casting, improper cooling happens and the product grain becomes unable to maintain the uniformity in growth rate. If there is a proper design of the die the grain growth can be maintained.
In this article, you have learned about what is forging, its definition, types, advantages, and disadvantages with the most common defects produced. If you like this piece of information then don’t forget to like and share it.