Can you imagine the world without plants and trees? No, you can’t, so can’t you imagine your surroundings without fasteners. Yes, they play very essential and vital role in this engineering world. Whenever you heard the word ‘fasteners’ there must be popup in your mind that it must be some screws, bolts or nuts. Yes it is, but there are many more fasteners which we are going to know about in this article.
So on this tone let’s begin to understand what really a fastener is?
Fastener is a hardware device which is used to join or holds materials together generally as a non-permanent joint. Yes, joint can be non-permanent or permanent; the joined components can easily be separated without damaging the joint in the former one and the joint gets damaged or reduces the strength in case of later one.
How permanent and non-permanents joints can be created?
Well generally fasteners are used to create non-permanents joints through Screws, bolts, nuts, washers, cotter joint etc.
And some permanent joints through the process which includes welding, riveting, soldering, brazing etc.
Importance of Fasteners
Have you heard about Boeing 747 jet airline? Yes, an American wide figure commercial jet airline often known as ‘Jumbo jets’, which have around 30 lakhs fasteners out of 60 lakhs parts. Fastener is a main hardware component which is used nearly everywhere, be it your door hinge or some house hold appliance, be it automobile, machineries, construction, infrastructure or all other items which require assembly will certainly have fasteners to affix them. What if a single fastener gets loose or broke down? It will surely affect the entire system or causes adverse consequences. So the strength, durability, rigidity depends upon the kind of material are we going to use or what should be the coating on it or what should be the dimension of it, because selection of correct fasteners will reduce the stress concentration which will reduce the fatigue. There are varieties of fasteners available in the market each with a specific reason to use which can be ferrous, non-ferrous or even plastic fasteners these days.
Types of Fasteners
1. Bolts and Nuts

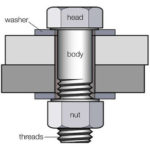
A bolt is a threaded fastener which is always coupled with a nut. Bolts have external male thread and nuts have internal male thread.
A bolt comprises of a head, cylindrical body and threads along its length. Bolts are generally have the flat head which means there is no grove on the head. It generally has the design on its periphery to get driven by the wrench tool and same goes for the nut.
2. Screws

These are the fasteners which create their own threads while fastening into the material. They typically have a head, and a shank with a helical threads .They have different types of head style and recess or drive style such as slotted, Pozidriv, Phillips, hex, Torx, Robertson etc.( to know more about this, consider the previous article) .
To know more about screws click the link given below:
Different Types of Screws in Fastening Process
3. Washers

These are the thin plate, disc shape with a hole in the middle and generally the outer diameter is twice of the inner, which is used to distribute load over which it is fasten such as on screw or nut. These can also be used as a spacer, locking device, wear pad etc. in many applications. It can be of metal, plastic or rubber according to the requirement.
4. Rivets

It is a permanent fastener, consist of head, shank and tail, which means it cannot be disassemble without damaging the joints. The process by which two material join together by applying force, can be hand driven or power driven, known as riveting. They are very strong in nature.
Also Read:
- 37 Types of Hammers that You Don’t Know?
- 6 Types of Screwdrivers – Everyone Must Know
- Different Types of Screws Heads – That You Must Know
5. Anchors Fasteners

These are widely used in construction and masonry or stone industries and are used to connect structural and non- structural material to the concrete or other materials. This is generally installed by drilling a larger hole, compare to the fastener diameter, and in the base material and then the anchor is inserted into the hole to a depth known as embedment depth. These are generally of two types: mechanical anchor fasteners and chemical anchor fasteners.
6. Inserts

These are the strong threads typically cylindrical in shape also known as thread bushing and are used for multiple purpose such as securing a long lasting connection between the various materials or to repairing stripped threads. These are generally used to distribute loads from small diameter of screw to the larger diameter of the inserts.
7. Snap Rings

These are also known as retaining rings and are the small metal rings that broken at one end of the circle , at the end of the circle there is a grooved shape which are used to hold and grip components onto a shaft while setting into a machined groove. They are commonly found in car engine parts, shocks absorber.
8. Clevis Pins and Cotter Pins

These are the steel pins or a head with a cylindrical shaft. These are used to hold machines components in accurate position or alignment. They consists a hole in the shaft in which a cotter pin is inserted and bend to act like a staple.
Also Read:
- Difference Between Nuts and Bolts
- Difference Between Bolt and Screw
- 24 Most Common Types of Pliers and Their Uses (With Pictures)
Material of a Fastener
When you are done with the selection of the best type of fasteners for your project, it’s come to the second most important criteria of material selection. Each and every project requires different materials depending upon various factors such as environmental conditions, corrosion nature, vibrations, strength, durability, and many other factors to keep your fastener fit for the job.
About 90% of our surroundings are of steel fasteners. It could be of carbon steel, stainless steel, alloy steel, etc. there are varieties of them because of having high degree of formability, durability, tensile strength and coped with relatively inexpensive to fabricate. It is generally processed with zinc or chromium plating.
1. Carbon Steel Fasteners
You must have seen black color fasteners while doing projects, this black color is due to the carbon content. The percent of carbon can vary upto 2.1% by weight from low- carbon steel to high carbon steel. These are used widely in automobile, oil and gas, ship buildings Industries, because of having robust construction, tensile strength, durability and resistance towards adverse environmental conditions.
Grades 2,5, 8, are typically the standards for these carbon steel fasteners
Now the question is that what are these grades and how to identify them?
Well for that we must look onto the head of the fasterner. To identify the grades we must look for the radial lines over it. If there are no lines then it’s a grade 2 which is low or medium carbon steel, if it have 3 radial lines then it’s a grade 5 which is medium carbon steel and are widely used in automotive applications, and if its have 6 radial lines it’s a medium carbon alloys which are generally used in vehicle suspension system .

2. Stainless Steel Fasteners

Mainly It is an alloy of low grade carbon and with 10.5% or more chromium by weight and some other elements. The chromium content leads to high degree of corrosion resistance. The low carbon content prevents it from being hardened, hence making them stronger than grade 2 but not as much of as grade 5 and grade 8. They also show shining properties. They are inexpensive, readily available, and attractive and are used in households to automobile industries.
3. Aluminum Fasteners

They are the lightweight fasteners and are used where weight is constrained and can be alloyed into many other materials to increase its strength. Acceptance to hot and cold temperatures is the USP of these fasteners. It is naturally corrosion resistance and non-magnetic.
4. Titanium Fasteners

Because of having good corrosion resistance property and sustainability at high temperature these fasteners are chiefly used in aircraft, petrochemical industries, racing car industries.
5. Brass and Bronze Fasteners

These are the electrically conductive copper alloy. Since bronze is a non-magnetic and highly resistant to corrosion these are widely used in ship buildings. They are not so common in use because of their high cost. Brass generally used for aesthetic purpose rather than strength. Brass is also a corrosion resistance material.
6. Non-metallic Fasteners

These are lightweight, non- conductive fasteners with low strength. These can’t sustain long in adverse environmental conditions. These are generally used for aesthetic purpose. Some non- metallic materials are nylon, PVC, polypropylene, neoprene etc.






This has being first class topic for a beginner like me. Am give me the knoweldge I wanted…
Thankyou..Melvyn