
When comparing the 2-stroke engine vs 4-stroke engine, it’s essential to understand what sets these engine types apart. Each has unique benefits, applications, and performance characteristics, making them suitable for different machines, from motorcycles and lawn equipment to cars and boats. In this article, we’ll dive into the differences between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines, covering their working principles, advantages, disadvantages, typical uses, and more. By the end, you’ll have a clear picture of which engine type is the best fit for your needs.
What is a 2-Stroke Engine?
A 2-stroke engine is an engine that completes a power cycle with two strokes (movements) of the piston during one crankshaft rotation. This cycle includes a compression stroke followed by an exhaust stroke, with both steps delivering power in just two piston movements. This simplicity makes 2-stroke engines popular in machines where speed and power-to-weight ratio are critical.
How Does a 2-Stroke Engine Work?
- Compression Stroke: As the piston moves up, it compresses the air-fuel mixture in the combustion chamber while simultaneously drawing a fresh fuel-air mixture into the crankcase.
- Power Stroke: At the top of the compression stroke, the spark plug ignites the mixture, forcing the piston down. The exhaust port opens to release the exhaust gases, while the intake port allows fresh fuel and air to enter, preparing for the next cycle.
Key Characteristics of 2-Stroke Engines:
- Lightweight and Compact: With fewer moving parts, 2-stroke engines are generally smaller and lighter.
- High Power-to-Weight Ratio: They generate more power relative to their size, ideal for high-speed applications.
- Simple Design: The fewer parts mean they are easier to repair and maintain.
What is a 4-Stroke Engine?
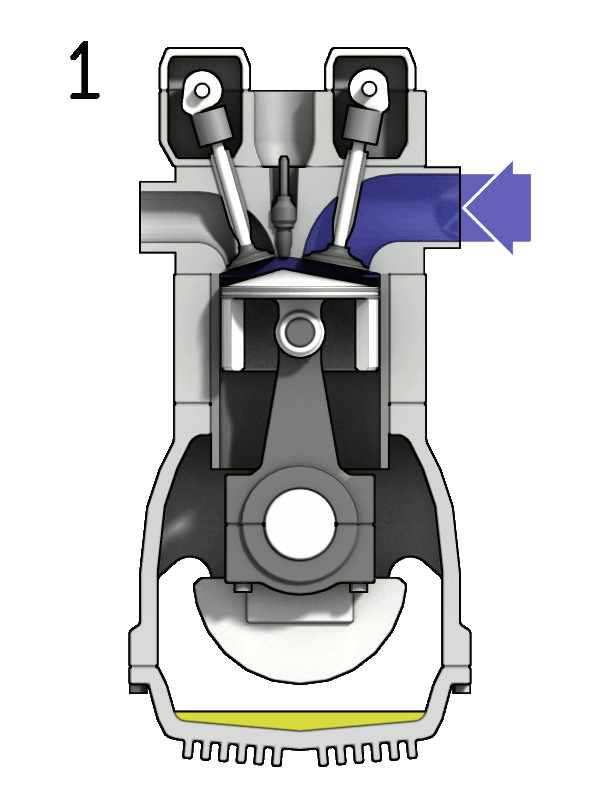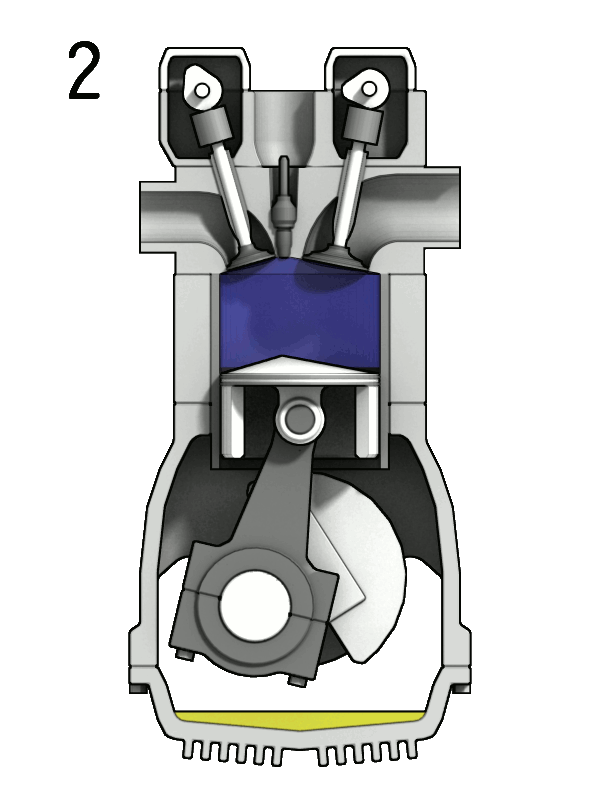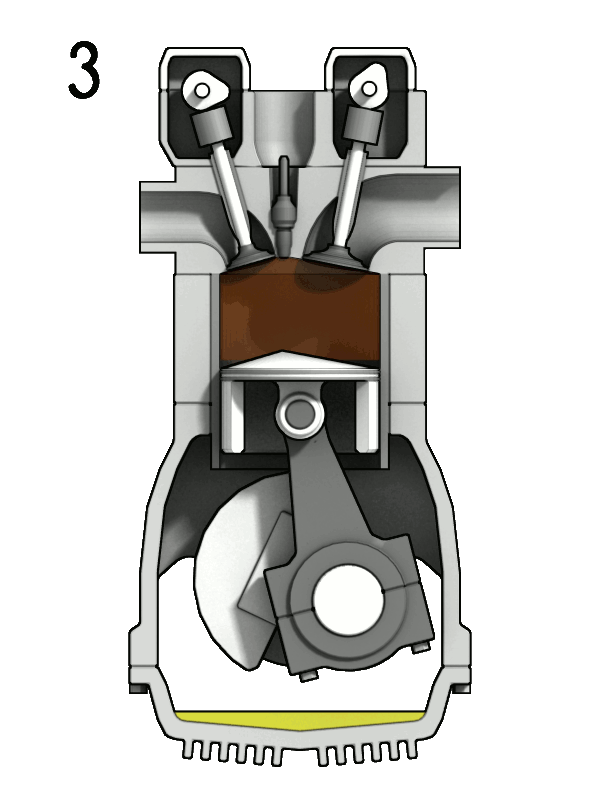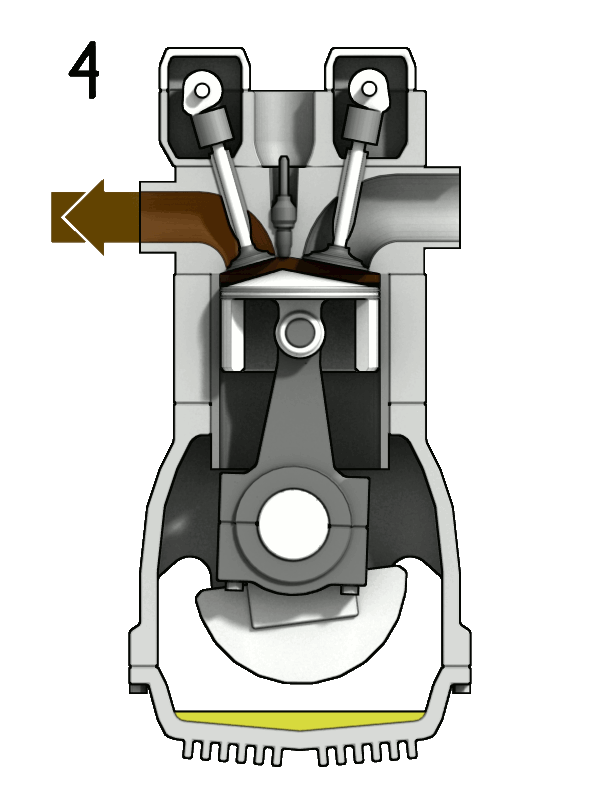
A 4-stroke engine completes its power cycle in four distinct stages—intake, compression, power, and exhaust—over two crankshaft rotations. This design allows for more controlled fuel combustion and efficient power delivery, making 4-stroke engines the go-to choice for vehicles, machinery, and other applications where longevity and fuel efficiency are crucial.
How Does a 4-Stroke Engine Work?
- Intake Stroke: The intake valve opens as the piston moves down, drawing in a fuel-air mixture into the combustion chamber.
- Compression Stroke: The intake valve closes, and the piston moves up, compressing the mixture to increase power potential.
- Power Stroke: At the peak of compression, the spark plug ignites the mixture, pushing the piston down to produce power.
- Exhaust Stroke: The exhaust valve opens, allowing the spent gases to exit as the piston moves up, clearing the chamber for a new cycle.
Key Characteristics of 4-Stroke Engines:
- Fuel Efficiency: With a more complete burn cycle, 4-stroke engines are typically more fuel-efficient.
- Durability and Longevity: The controlled combustion process and less frequent wear on components mean 4-strokes often last longer.
- Lower Emissions: They produce fewer emissions, making them more environmentally friendly.
2-Stroke vs 4-Stroke Engine: Key Differences
Here’s a closer look at the primary differences between 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines:
| Aspect | 2-Stroke Engine | 4-Stroke Engine |
| Power Cycle | Completes in two strokes | Completes in four strokes |
| Power Output | Power delivered every crankshaft rotation | Power delivered every other crankshaft rotation |
| Fuel Efficiency | Consumes more fuel, less efficient | More efficient, uses fuel more completely |
| Weight | Lightweight, fewer parts | Heavier, more complex design |
| Emissions | Higher emissions, more pollutants | Lower emissions, environmentally friendly |
| Noise Level | Louder due to frequent exhaust cycles | Quieter operation |
| Applications | Used in lightweight machinery like chainsaws | Common in cars, motorcycles, and large equipment |
| Cost | Generally lower initial and maintenance costs | Higher upfront and maintenance costs |
Advantages and Disadvantages of 2-Stroke Engines
Advantages of 2-Stroke Engines:
- Higher Power-to-Weight Ratio: Due to power being generated every rotation, 2-stroke engines are powerful for their size.
- Lightweight Design: With fewer components, these engines are lighter, which is useful for portable machinery and vehicles.
- Simpler Mechanics: Their straightforward design makes them easier to maintain and repair.
Disadvantages of 2-Stroke Engines:
- Lower Fuel Efficiency: Due to incomplete combustion cycles, 2-strokes consume more fuel.
- Higher Emissions: The rapid cycle of fuel intake and exhaust results in higher emissions, releasing unburned fuel into the air.
- Shorter Lifespan: 2-stroke engines wear out faster due to higher RPMs and constant power delivery, requiring more frequent maintenance.
Advantages and Disadvantages of 4-Stroke Engines
Advantages of 4-Stroke Engines:
- Greater Fuel Efficiency: With a longer combustion cycle, fuel is used more effectively, reducing overall fuel costs.
- Lower Emissions: 4-stroke engines produce fewer pollutants, making them better for the environment.
- Durable and Long-Lasting: The slower wear on parts increases the engine’s lifespan.
Disadvantages of 4-Stroke Engines:
- Heavier Design: With more components and a more complex design, 4-stroke engines are bulkier and heavier.
- Higher Cost: 4-stroke engines are more expensive to manufacture and repair due to additional components and complexity.
- Lower Power Density: Since power is only delivered every other crankshaft rotation, 4-stroke engines have a lower power-to-weight ratio compared to 2-strokes.
Typical Applications of 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engines
Understanding where each engine excels helps illustrate their practical uses:
2-Stroke Engine Applications:
- Power Tools: Chainsaws, leaf blowers, and other small equipment benefit from the lightweight design and high power output.
- Motorcycles and Dirt Bikes: Smaller, lightweight motorcycles and dirt bikes often use 2-stroke engines for speed and maneuverability.
- Small Watercraft: Jet skis and smaller boats may use 2-stroke engines for the power and speed they provide.
4-Stroke Engine Applications:
- Automobiles: Most cars, trucks, and SUVs rely on 4-stroke engines due to their durability and fuel efficiency.
- Motorcycles and ATVs: Heavier motorcycles and all-terrain vehicles often use 4-stroke engines for a more controlled, durable ride.
- Generators and Lawn Mowers: For longer-lasting performance and lower emissions, generators, mowers, and other outdoor equipment often use 4-stroke engines.
Which Engine is Right for You: 2-Stroke or 4-Stroke?
Choosing between a 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine depends on your specific needs and preferences:
- For Power in Compact Machines: A 2-stroke engine is ideal for situations where weight and space are at a premium and where high power is required, like in chainsaws or dirt bikes.
- For Fuel Efficiency and Durability: A 4-stroke engine is preferable for applications that require long-term usage, such as in cars, lawnmowers, or generators. They offer improved fuel efficiency, lower emissions, and greater durability, making them cost-effective in the long run.
- Environmental Impact: If emissions and noise are concerns, 4-stroke engines are usually better, meeting more stringent emission standards than 2-stroke engines.
Conclusion
In the debate between 2-stroke vs 4-stroke engines, the choice ultimately depends on your requirements for power, efficiency, weight, and environmental impact. 2-stroke engines are known for their high power-to-weight ratio, lightweight construction, and simplicity, making them ideal for small, high-speed machines. 4-stroke engines, on the other hand, offer better fuel efficiency, reduced emissions, and longer-lasting performance, making them ideal for vehicles, lawn equipment, and other long-term applications.
Understanding these differences can help you choose the right engine type for your equipment, balancing the need for speed, power, and efficiency. Whether you’re revving up a dirt bike or maintaining a lawn mower, knowing the strengths of 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines will help you make an informed, efficient choice.








