When it comes to understanding engines, particularly in motorcycles, scooters, and small machines like lawnmowers, the terms 2-stroke engine and 4-stroke engine often come up. But what exactly is the difference between a 2-stroke engine and a 4-stroke engine? Which one is better for your needs?
This article will break down the key differences, benefits, and drawbacks of both types of engines, helping you make an informed decision whether you’re buying a vehicle or learning about engines.
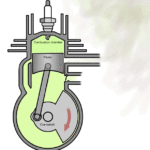
What is a 2-Stroke Engine?
A 2-stroke engine completes a power cycle with two strokes (up and down movement) of the piston during only one revolution of the crankshaft. It combines the intake and compression stroke into one, and the power and exhaust stroke into another, making it a simpler, more efficient process in some applications.
How a 2-Stroke Engine Works:
- Stroke 1: Intake and Compression – As the piston moves up, it compresses the air-fuel mixture while simultaneously creating a vacuum that pulls more air-fuel into the crankcase.
- Stroke 2: Power and Exhaust – When the piston reaches the top of the cylinder, the spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing an explosion that pushes the piston back down, delivering power. At the same time, the exhaust gases are expelled.
Pros of a 2-Stroke Engine:
- Lightweight and Simple: With fewer moving parts, 2-stroke engines are generally lighter and less complex, making them ideal for smaller vehicles like dirt bikes or chainsaws.
- Higher Power-to-Weight Ratio: Since every revolution of the crankshaft produces power, 2-stroke engines can generate more power than their 4-stroke counterparts of similar size.
- Lower Cost: Fewer parts make these engines cheaper to manufacture and maintain.
Cons of a 2-Stroke Engine:
- Higher Fuel Consumption: Because 2-stroke engines fire once per revolution, they tend to burn more fuel than 4-stroke engines.
- More Pollution: Without a dedicated exhaust stroke, some unburnt fuel escapes with the exhaust, leading to higher emissions.
- Shorter Lifespan: The simpler design often leads to quicker wear and tear on the engine components.
What is a 4-Stroke Engine?
A 4-stroke engine requires four strokes of the piston (two revolutions of the crankshaft) to complete one power cycle. It separates the intake, compression, power, and exhaust strokes into distinct movements, resulting in a more efficient process.
How a 4-Stroke Engine Works:
- Stroke 1: Intake – The piston moves down, drawing in a mixture of air and fuel.
- Stroke 2: Compression – The piston moves up, compressing the air-fuel mixture in the cylinder.
- Stroke 3: Power – The spark plug ignites the compressed mixture, causing an explosion that forces the piston down, generating power.
- Stroke 4: Exhaust – The piston moves back up, expelling the exhaust gases through the exhaust valve.
Pros of a 4-Stroke Engine:
- Better Fuel Efficiency: Since the fuel burns more completely, 4-stroke engines are more fuel-efficient than 2-stroke engines.
- Lower Emissions: The dedicated exhaust stroke helps reduce pollution by ensuring more complete combustion and fewer unburnt hydrocarbons are released.
- Longer Lifespan: With a more balanced and controlled operation, 4-stroke engines tend to last longer and are more durable.
Cons of a 4-Stroke Engine:
- Heavier and More Complex: With more parts (valves, camshaft, etc.), 4-stroke engines are bulkier and heavier.
- Lower Power-to-Weight Ratio: Since power is produced once every two revolutions, 4-stroke engines have less power output relative to their size.
- Higher Maintenance Costs: The increased complexity means there are more parts that can wear out or fail over time, leading to higher maintenance costs.
Key Differences Between 2-Stroke and 4-Stroke Engines
| Aspect | 2-Stroke Engine | 4-Stroke Engine |
| Power Stroke | Every revolution of the crankshaft | Every two revolutions of the crankshaft |
| Efficiency | Lower fuel efficiency | Higher fuel efficiency |
| Emissions | Higher emissions | Lower emissions |
| Power-to-Weight Ratio | Higher (more power per size) | Lower |
| Durability | Shorter lifespan | Longer lifespan |
| Maintenance | Cheaper to maintain, but needs more frequent servicing | Higher maintenance costs, less frequent |
| Weight | Lighter and more compact | Heavier and bulkier |
Which Engine is Better for You?
The choice between a 2-stroke and 4-stroke engine depends on your specific needs:
- For Power and Simplicity: If you need a lightweight engine with high power output, such as for dirt bikes, lawnmowers, or small recreational vehicles, a 2-stroke engine is a good option.
- For Fuel Efficiency and Durability: If you prioritize fuel economy, lower emissions, and engine longevity, especially in motorcycles, cars, or larger equipment, a 4-stroke engine is the better choice.
Conclusion
Both 2-stroke and 4-stroke engines have their own advantages and drawbacks. While 2-stroke engines offer simplicity and more power for their size, they are less fuel-efficient and produce more emissions. On the other hand, 4-stroke engines offer better fuel economy, are more environmentally friendly, and have a longer lifespan, though they are heavier and more complex.
Understanding the difference between these engines is essential when choosing the right vehicle or equipment for your needs. Whether you prioritize power, efficiency, or durability, this guide should help you make the best decision.
FAQs: Frequently Asked Questions
1. Why do 2-stroke engines produce more pollution?
2-stroke engines mix oil with fuel for lubrication, and because they lack a dedicated exhaust stroke, some unburnt fuel is released into the environment, causing higher emissions.
2. Are 2-stroke engines still used today?
Yes, 2-stroke engines are still used in various applications such as off-road motorcycles, chainsaws, and outboard motors where high power and light weight are prioritized.
3. Why do 4-stroke engines last longer?
The controlled, slower operation of a 4-stroke engine places less wear on engine components, resulting in a longer lifespan and more efficient use of fuel and oil.







thanks for the info!
Please tell me why four stroke engine has less wear and tear instead it has more frictional parts..??
Because they run at lower rpm.
Bcoz in a 2 stroke engine, every second stroke is a power stroke… While in 4 stroke engine, power stroke comes after 4 strike movements..
Very useful information so thanks for this information
Well explained . Thank you
Thank you for this simple and important explanation
Could timing be more difficult to fix on a 4-stroke then a 2 stroke?