Artificial Intelligence (AI) is no longer a futuristic concept — it is actively reshaping mechanical engineering design, manufacturing, maintenance, and product development.
From AI-driven generative design to predictive maintenance in smart factories, mechanical engineers are leveraging machine learning, data analytics, and automation to create faster, smarter, and more efficient systems.
This guide explains how AI is transforming mechanical engineering, with real-world applications, tools, benefits, and future trends.
1. AI in Mechanical Design & Generative Engineering
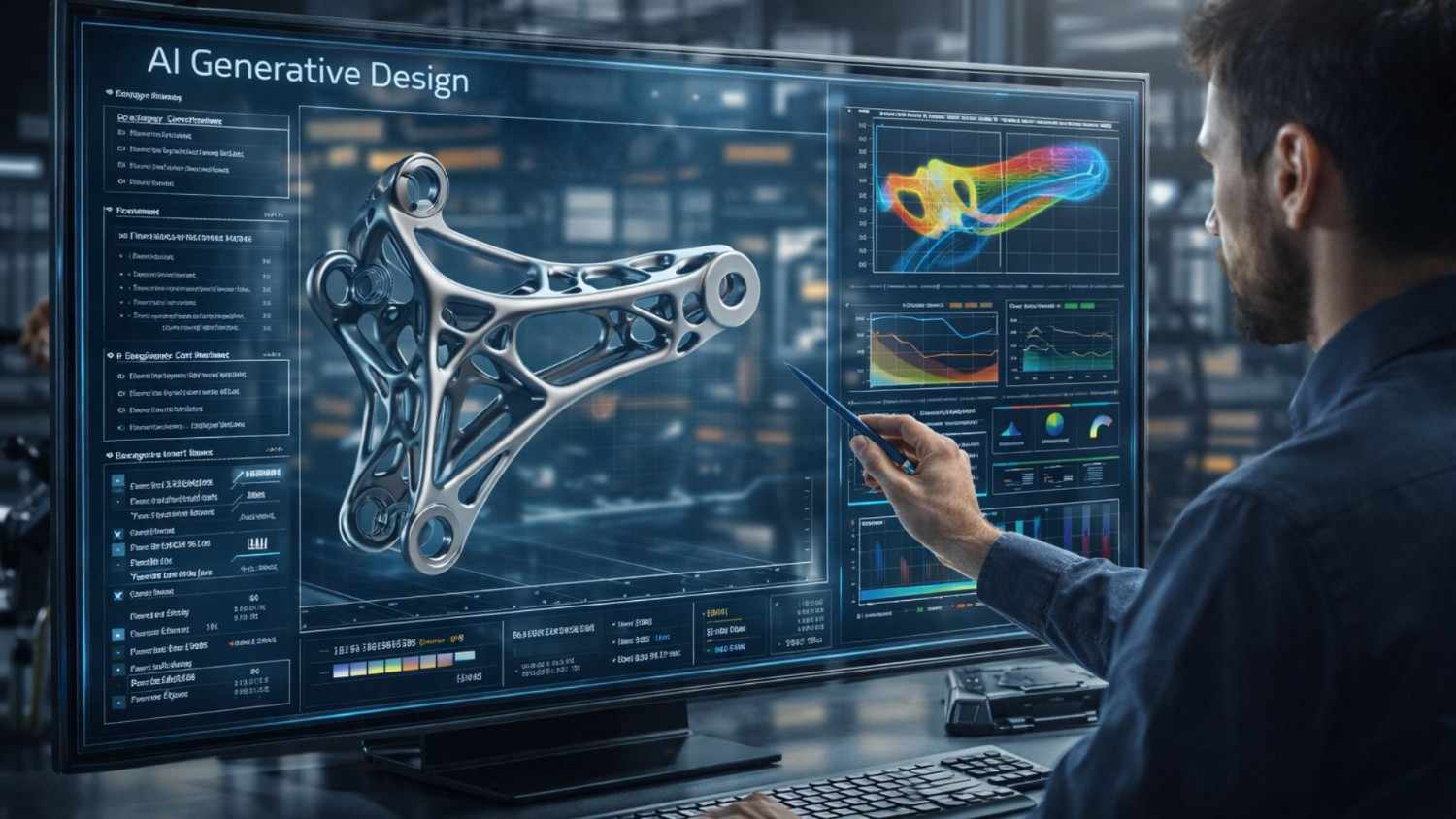
What Is Generative Design?
Generative design uses AI algorithms to automatically create optimized design alternatives based on:
- Load conditions
- Material properties
- Manufacturing constraints
- Cost targets
Instead of manually designing a part, engineers define requirements — and AI generates multiple optimized geometries.
Key Tools Used
- Autodesk Fusion 360 (Generative Design Module)
- Siemens NX
- ANSYS (AI-enhanced simulation)
Benefits
- 30–60% weight reduction in structural components
- Reduced material usage
- Faster design iterations
- Improved structural performance
Example: Aerospace brackets redesigned using AI have achieved significant weight savings while maintaining strength.
2. AI in Smart Manufacturing & Industry 4.0
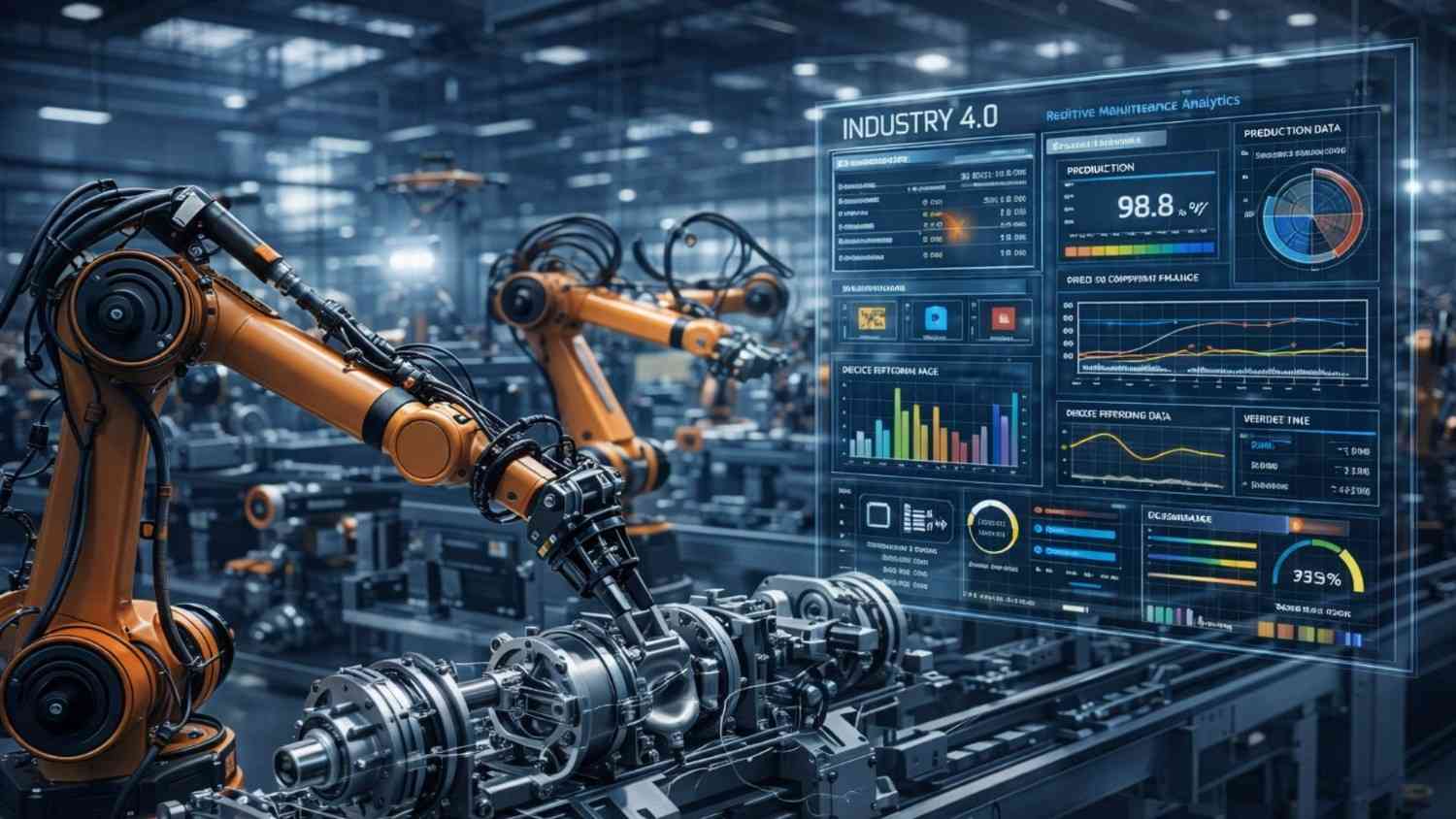

AI plays a major role in modern Industry 4.0 systems.
Applications in Manufacturing
1. Predictive Maintenance
AI models analyze vibration, temperature, and noise data to predict equipment failure before it occurs.
Used in:
- CNC machines
- Turbines
- Compressors
- Automotive assembly lines
2. AI-Based Quality Control
Computer vision systems detect:
- Surface defects
- Dimensional deviations
- Weld imperfections
3. Process Optimization
Machine learning optimizes:
- Cutting parameters
- Tool paths
- Cycle times
- Energy consumption
Result: Reduced downtime, lower scrap rates, and higher productivity.
3. AI in Robotics & Automation
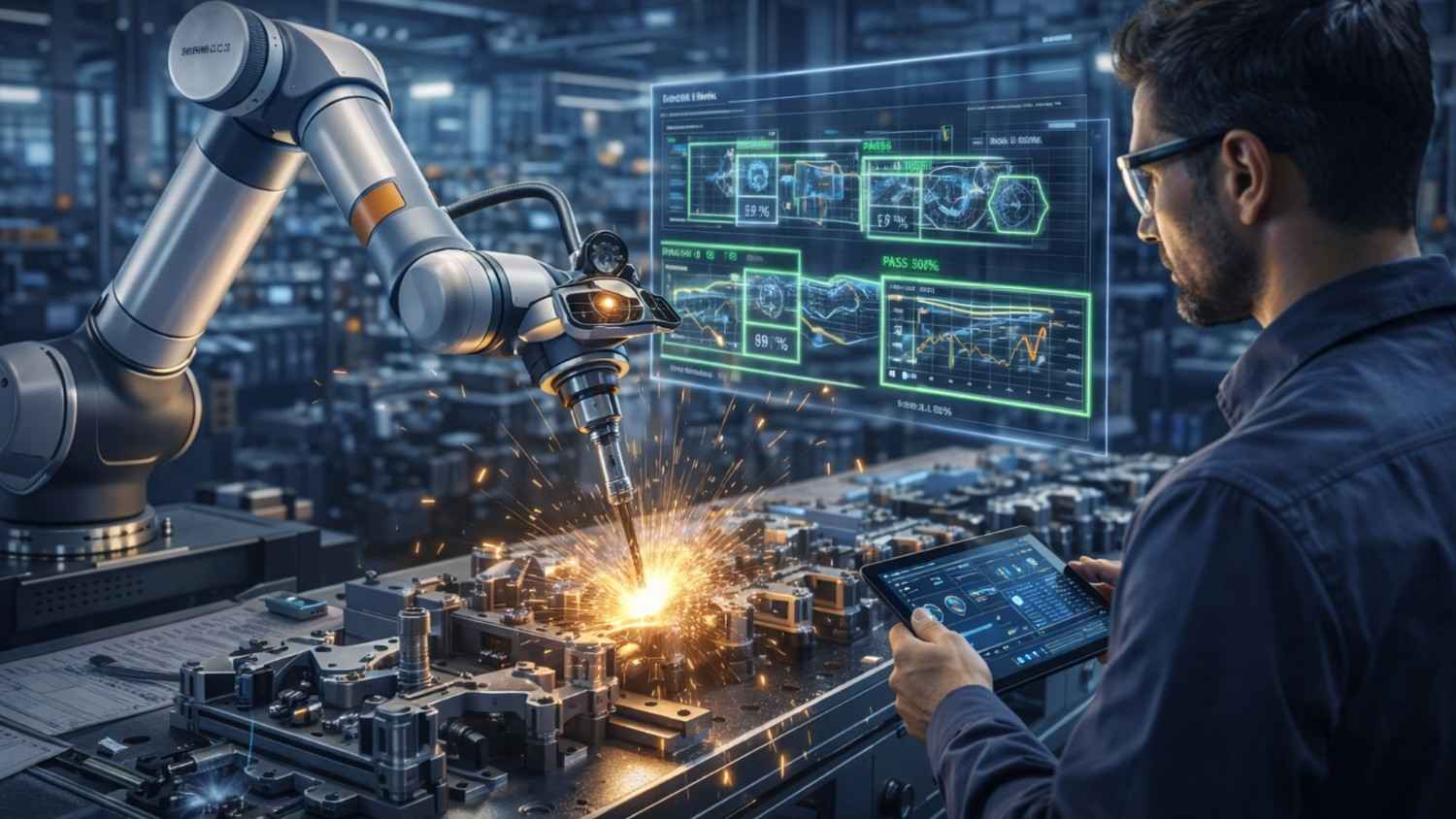
AI enhances robotic systems used in:
- Welding
- Assembly
- Material handling
- Inspection
Modern robots can:
- Adapt to variations in parts
- Learn from data
- Work safely alongside humans (cobots)
AI enables real-time path correction and intelligent motion planning.
4. AI in Thermal & Fluid Engineering
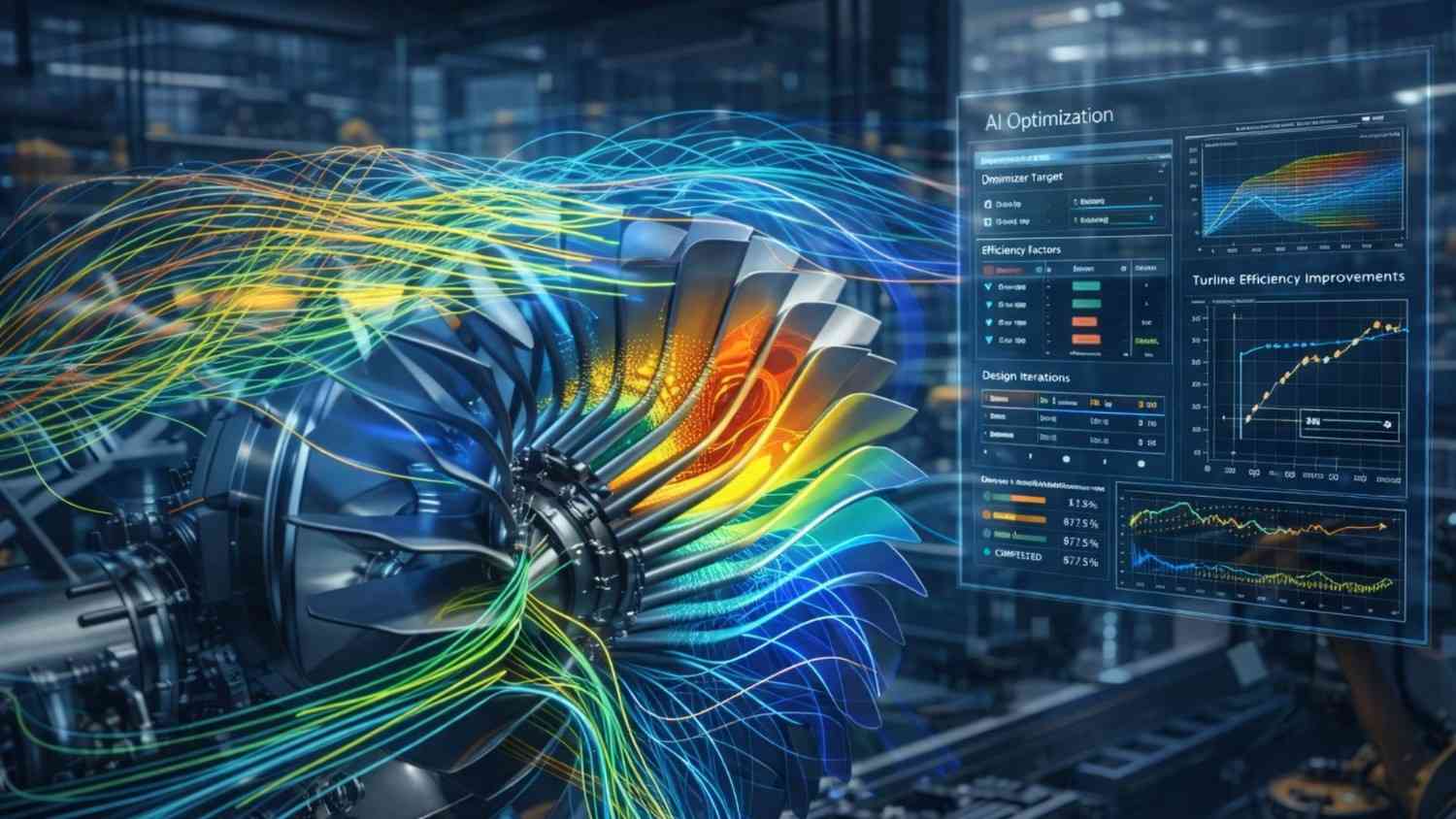
AI accelerates CFD and thermal simulations by:
- Reducing computation time
- Creating surrogate models
- Predicting fluid flow patterns
Instead of running thousands of simulations, AI models approximate results instantly — saving time in:
- HVAC system design
- Turbine blade cooling
- Automotive aerodynamics
- Heat exchanger optimization
5. AI in Electric Vehicles (EVs) & Automotive Engineering
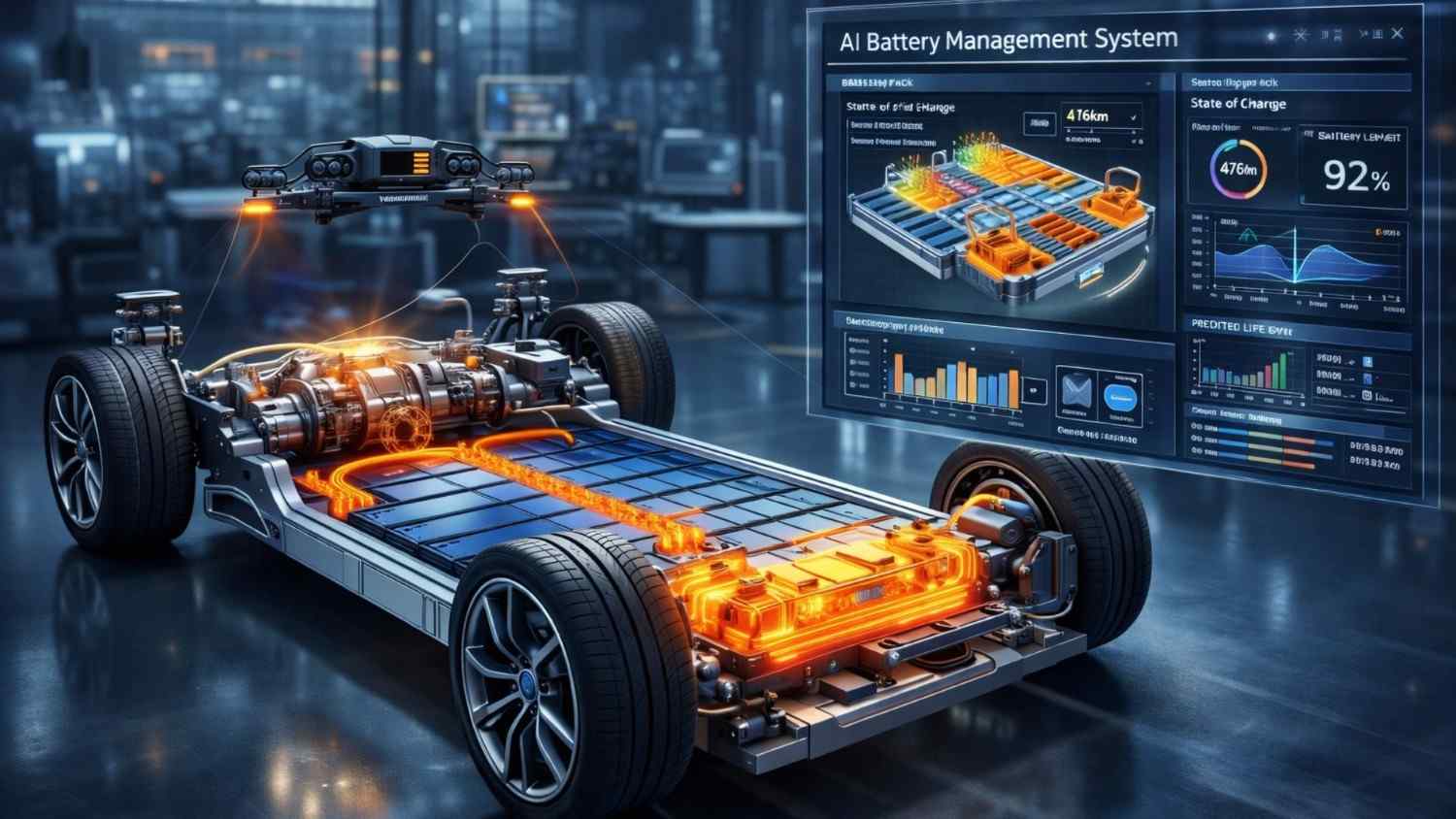

AI is revolutionizing automotive engineering through:
Battery Management Systems (BMS)
AI predicts:
- State of charge (SOC)
- State of health (SOH)
- Thermal runaway risks
Autonomous Systems
AI integrates:
- LiDAR
- Radar
- Computer vision
Powertrain Optimization
AI enhances:
- Motor efficiency
- Regenerative braking
- Thermal management
Mechanical engineers now collaborate closely with data scientists in EV development.
6. AI-Driven Predictive Maintenance in Heavy Industries
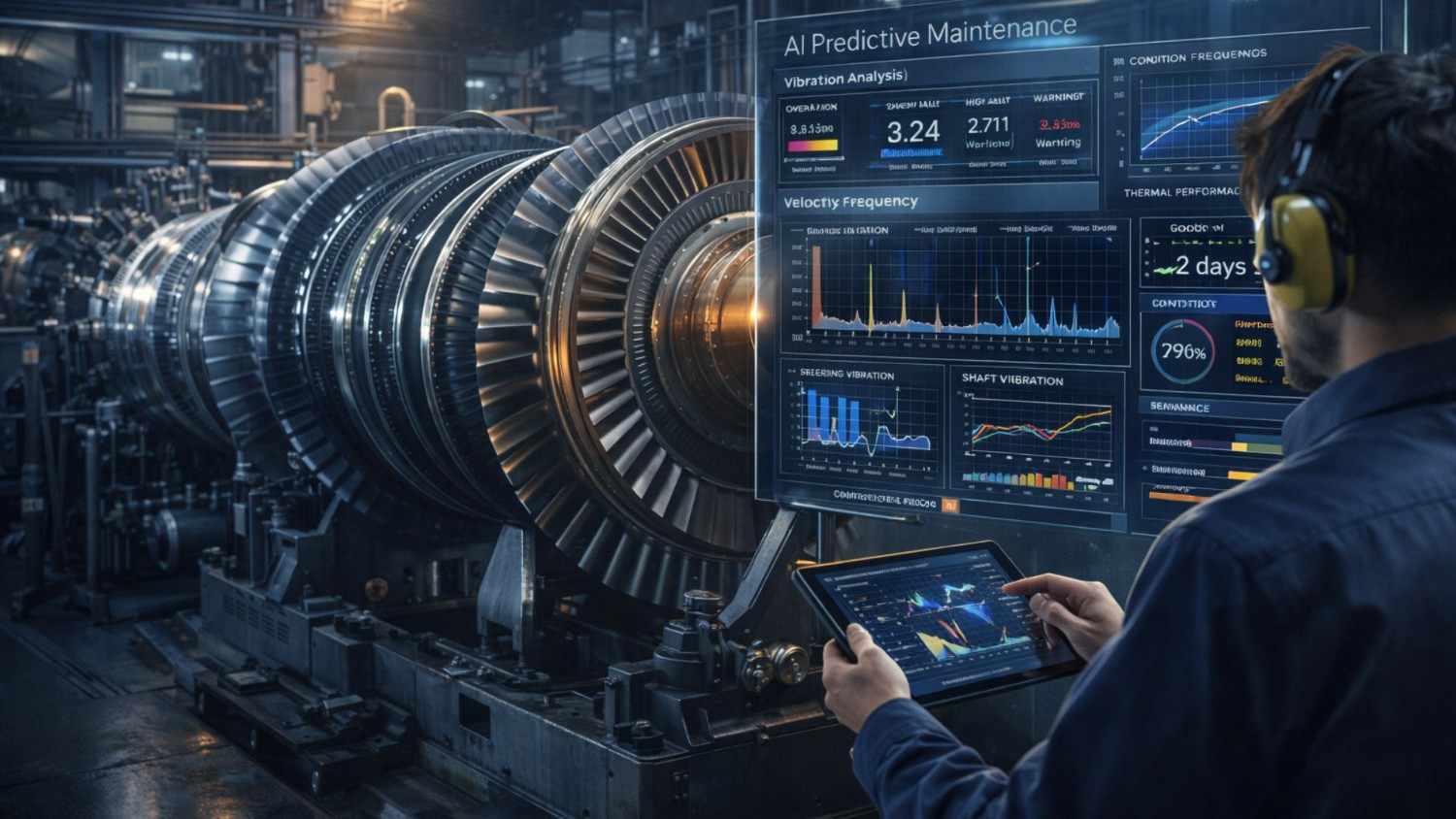

Industries benefiting:
- Oil & Gas
- Power plants
- Aerospace
- Railways
AI models detect:
- Bearing faults
- Shaft misalignment
- Cavitation
- Imbalance
This reduces:
- Unexpected failures
- Maintenance costs
- Safety risks
7. AI + Digital Twin Technology
A Digital Twin is a virtual replica of a physical system.
AI enhances digital twins by:
- Continuously updating models with sensor data
- Predicting performance degradation
- Optimizing operational parameters
Used in:
- Smart factories
- Aircraft engines
- HVAC systems
- Industrial plants
Key Benefits of AI in Mechanical Engineering
| Benefit | Impact |
| Faster Design | Reduced development cycle |
| Lower Costs | Less material & downtime |
| Higher Accuracy | Better simulations |
| Improved Safety | Early fault detection |
| Energy Efficiency | Optimized systems |
Challenges of AI Adoption
- High initial investment
- Need for data infrastructure
- Cybersecurity concerns
- Skill gap in AI & data science
- Resistance to change
Mechanical engineers must now develop data literacy and programming skills.
Future of AI in Mechanical Engineering
In the next decade, we will see:
- Autonomous factories
- Fully AI-optimized product lifecycle
- AI-assisted materials discovery
- Human-AI collaborative design
- Self-healing mechanical systems
AI will not replace mechanical engineers — but engineers who use AI will replace those who don’t.
Conclusion
Artificial Intelligence is transforming mechanical engineering from a traditional design-based discipline into a data-driven, intelligent engineering ecosystem.
Whether in generative design, predictive maintenance, robotics, or EV systems, AI is increasing efficiency, reducing costs, and accelerating innovation.
Mechanical engineers who embrace AI tools, simulation automation, and machine learning will lead the future of smart engineering.








