Introduction:
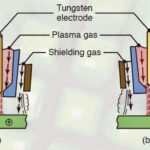
Atomic Hydrogen Welding is a welding process that uses two tungsten electrodes and atomic hydrogen as a shielding gas for welding. It is one of the most superior welding processes that provides a smooth weld finish, perfect for Industrial usage. The reason for calling the process atomic hydrogen welding is because the arc produced is sufficiently high to break hydrogen molecules into atoms. The temperature during the welding can go as high as 6500o F. Hence, personal protective equipment is necessary during the process. This article will discuss this joining process in detail, discussing its history, working principle, process variables, advantages, disadvantages, and application. So, let us get started.
History and Development

It all started with producing a continuous arc, which created a different variant of the joining process. In 1800, Humphry Davy discovered a short-pulsed electric arc. A Russian scientist named Vasily Petrov developed a continuous electric arc in 1802 and proposed its application in welding. After creating an electric arc and proposed application, CL Coffin was the first person to introduce welding under Inert conditions in the 1890s. The proposed idea was difficult to achieve and was not accomplished till 1900. By the 1940s, tungsten and helium started where tungsten was used as electrode material and helium as an inert gas. Around 1940, Irving Langmuir invented atomic hydrogen welding by using tungsten electrodes with a Hydrogen shielding environment.
The Historical development, in brief, is as follows:
- 1800- The development of short-pulsed electric arc is done by Humphry Davy
- 1802- Development of continuous electric arc by Vasily Petrov and proposed the idea for usage in welding
- 1890- An Idea of using Inert gas as a shielding environment is proposed
- 1900s- The usage of shielding gas as an Inert gas atmosphere for welding start
- 1940s (around)- Irving Langmuir developed atomic hydrogen welding, where atomic hydrogen is used as shielding gas during the welding process.
Main Parts of Atomic Hydrogen Welding:
The Joining process consists of different parts that make up the complete mechanism. In this heading, we will be talking about these components in detail with their application. The components are essential for the successful operation of atomic hydrogen welding. The main parts of this Joining process are as follows:

1. Tungsten Electrode:
In this Joining process, two welding electrodes are used, which are at an angle with each other. These are inclined with a definite angle to produce a stable electric arc.
2. Electrode Holder:
The electrode holders are used to hold the tungsten electrode, which is also inclined as the tungsten electrode.
3. Nozzles:
Nozzles are connected with the Hydrogen cylinder, which takes out atomic hydrogen during the Joining process. They are annular and serves the purpose of providing the shielding gas.
4. AC Power Supply:
Power Supply is used to produce the electric arc between the electrodes by generating the current and developing the required heat. AC power supply is preferred over DC Power supply because equal heat is required at both ends.
5. Hydrogen gas Cylinder:
The cylinder is filled with hydrogen gas, which we will send to the required place during the Joining process.
6. Transformer:
The transformer must produce the electric arc and maintain it for the required period of time.
7. Pressure-regulating Valve:
A valve is present over the hydrogen cylinder to measure and regulate the pressure inside the cylinder. It is also connected with the Nozzle, which is used to supply the hydrogen gas at the required destination.
8. Filler Rod:
The usage of filler rods in this welding process is Optional. They are used as consumable electrodes and are used only when required.
9. Workpiece Plates:
These are the metal pieces that are to be joined through welding. Dirt, oxides, and other impurities are removed before welding the metal piece.
Also Read:
- What is Arc Welding – Definition, Types, Working, Advantages and Disadvantages
- What is Electron Beam Welding? – Complete Explanation
- What is Plasma Arc Welding? – Complete Explanation
AC vs DC Power Supply:
Before learning about the difference in applying these power supply for atomic hydrogen welding, let us first see what AC and DC power supply means.
1. AC Power Supply:
It stands for alternating current power supply. The power supply is AC when the electrical parameter, such as voltage, current, and impedance, is changing over time. In such a way, the change is positive in one half of the cycle and negative in another half of the cycle, which is most widely used in industrial applications.
2. DC Power Supply:
It stands for direct current power supply. It is a conventional electric energy source, where the electrical parameters such as current, voltage, and impedance (resistance here) are not changing over time. These find their application mainly in electrical instruments, welding instruments, Etc.
Now, you have understood the difference between these Power supply sources. Now, let us know the preference of usage in case of this joining process. Using an AC power supply instead of a DC power supply is that we have to maintain an equal amount of heat between the ends of electrodes to take the process correctly and produce a stable arc. AC power supply can easily achieve this requirement over the DC power supply. Hence during atomic hydrogen welding, an AC power source is used over the DC power source.
Working of Atomic Hydrogen Welding
This Joining process involves two tungsten electrodes, which produce an electric arc and hydrogen gas, which provides a shielding environment to save the weld pool from external contamination.

The process starts with creating an electric arc between the two electrodes (separated by nearly 1.5 mm) using the AC power supply. The electrodes are then separated slightly to stabilize the arc for a more extended period of time.
We can control the produced heat between the electrodes due to the arc by varying the distance between the electrodes. In the meantime, the nozzle will supply the hydrogen gas to produce a shielding environment around the weld pool to save it from external contamination. The shielding gas will also ensure the proper finish of the weld.
The Major advantage of hydrogen is that when it comes in contact with atmospheric oxygen, it will quickly form water vapor and suddenly vaporizes, protecting the weld from any external contamination. The name atomic hydrogen welding came from the fact that the molecular form of hydrogen used in the process changes to atomic hydrogen due to the amount of heat produced during the process. The temperature near the arc is around 6,000 °C, which is high enough to provide the necessary condition for converting molecular hydrogen to atomic hydrogen.
The following reaction will take place during this process:
H2 = H + H – 422 KJ (Endothermic Reaction)
When the molecular hydrogen is converted into atomic hydrogen, Energy equal to 422 KJ is required to achieve the change, while to convert the atomic hydrogen to molecular hydrogen, we will liberate Energy equal to 422 KJ in the process.
H + H = H2 + 422 KJ (Exothermic Reaction)
The overall heat produced during the process is used to create the weld pool, which then solidifies to form the finished product.
For a better explanation of Atomic Hydrogen Welding, watch the video given below:
Process Variables:
The process of atomic hydrogen welding is dependent upon various process variables that decide the final weld finish. The parameters decide how the process will occur from arc creation to production of shielding environment and joining of metal. In this heading, we will discuss different factors that play an important role in deciding the final weld finish. The process variables, which are the main deciding factor for this Joining process, are as follows:
1. Size of arc:
The Size of the arc is an important deciding factor for the successful completion of welding. The size of the arc depicts the intensity of the arc and the distance to which it affects. It also plays a major role in converting the molecular hydrogen into atomic hydrogen to shield during the joining process.
2. Contact of the Arc with Work:
The Arc contact with the workpiece is also important as this will provide an effective weld and good weld finish. There can be three different conditions for the contact of the arc with the work- Don’t contact, tangent to the surface, and piercing the surface. The first and third conditions might be a disadvantage in one way or the other. The 2nd condition is the perfectly critical condition to achieve a good weld finish.
3. Speed of Travel:
The travel speed of the arc and the current are also critical to stabilizing the arc. The overall process depends upon the arc and its stability during the joining process.
4. Current Setting:
The intensity of the current is important because it affects the overall power produced. Since the voltage difference is almost constant over time (apart from the direction), the current is the major deciding factor for producing and stabilizing the electric arc.
Apart from the factors mentioned above, various other factors play an essential role in deciding the proper weld finish, including the proper pressure of the released molecular hydrogen, nozzle diameter, Etc.
Parameters to Avoid in Atomic Hydrogen Welding
Various parameters are to be avoided during this Joining process to achieve a good weld finish. The parameters to avoid are as follows:
- Too little and too much weld according to the material that is required to be welded. Hence, we have to properly consider the required Heat that is to be produced during the Joining process. We denote too little Heat with the condition if too much time is taken for metal fusion.
- We can control the Intensity of the arc with the gap between the electrodes, which should not be too small or too large. This will lead to the production of a minimal amount of heat during the process.
- The Heat produced during the process should be medium, a small amount of heat creates a small weld pool, which is difficult to maintain, causes surface porosity, and causes uneven weld finish.
- As per the previous point, the Heat produced during the process should not be large enough to create a wide weld pool and produce a hole in the workpiece.
- If proper fusion is not taking place with the correct amount of Heat and arc, then change the welding speed or current setting (they can be increased).
- To weld soft metals with less melting temperature, the arc distance should produce a small amount of Heat.
- The produced arc should touch the weld metal to provide good welding and a proper weld finish.
Advantages Of Atomic Hydrogen Welding
Atomic hydrogen welding provides various advantages because of which it finds application in multiple industries. The advantage of this Joining process are as follows:
- The Weld formation is relatively faster than other welding processes.
- Hydrogen acts as a shielding gas, which also contributes to the production of heat. Hence, no separate shielding gas is required.
- The flames that are formed are intense and can be concentrated at a point.
- The electrode used remains cool during the process. Hence, the life of the electrode is increased.
- A small amount of adjustment can easily control the Process variables.
- Alloys can be easily welding by this welding process, by the use of atomic hydrogen.
Disadvantages of Atomic Hydrogen Welding:
The joining process has various advantages, but same as other joining processes, it also has some shortcomings that limit its application for some Industries. The disadvantages of this Joining process are as follows:
- The process is costly as compared to other Joining processes.
- The process is complicated as it should be performed with a skilled welder.
- We can deposit a large quantity of metal together in this Joining process.
- We can do this Joining process only in flat positions.
- The joining process is risky as hydrogen is a highly inflammable gas.
Applications:
The applications of the atomic hydrogen welding process are as follows:
- It is used as rapid welding process for metals such as stainless steel and other alloys.
- It can be used for welding most of the ferrous and non-ferrous metals.
- It is also perfect for welding thin sheets and other alloys.
- It is also used in precision welding processes, etc.
Frequently Asked Questions: FAQs
Q1: Is it possible to weld dissimilar metal with this Joining process?
Ans: It can weld dissimilar metals but will not be an effective process as there are various parameters that should be precisely controlled in order to achieve a proper weld finish.
Q 2: What is the full form of PPE kit and its use in this process?
Ans: PPE Kit stands for personal protective equipment kit. It is very important to protect yourself during the joining process as the temperature around the weld pool can reach as high as 35000 C.