Understanding the various parts of a car is essential for both drivers and automotive enthusiasts. This knowledge not only aids in vehicle maintenance but also enhances driving safety and performance. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the key components of a car, categorized into several main systems.
Main Parts of the Car and Their Functions

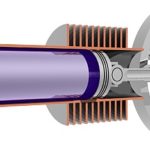
1. Engine Components
The engine is the heart of the vehicle, responsible for converting fuel into mechanical energy. Key parts include:
- Cylinder Block: The main structure housing cylinders where fuel combustion occurs. It serves as the foundation for the engine, supporting other components and maintaining alignment.
- Pistons: Move up and down within the cylinders, creating the necessary pressure for motion. Pistons are crucial in converting the energy from fuel combustion into mechanical work.
- Crankshaft: Converts the pistons’ linear motion into rotational motion to drive the wheels. The crankshaft plays a vital role in transmitting power from the engine to the drivetrain.
- Camshaft: Controls the opening and closing of engine valves, regulating air and fuel intake. Proper timing of the camshaft ensures efficient engine performance.
- Spark Plugs: Ignite the air-fuel mixture in gasoline engines to initiate combustion. Spark plugs are essential for starting the engine and maintaining smooth operation.
2. Transmission System
The transmission transmits power from the engine to the wheels, enabling the vehicle to move at varying speeds. It includes:
- Gearbox: Adjusts torque and speed by engaging different gear ratios. The gearbox allows the driver to control the vehicle’s speed and power output.
- Clutch: Connects and disconnects the engine from the transmission, allowing for smooth gear changes. In manual transmissions, the clutch is operated by the driver to shift gears.
- Drive Shaft: Transfers torque from the transmission to the differential. The drive shaft is a critical component in rear-wheel and all-wheel-drive vehicles.
- Differential: Distributes engine power to the wheels while allowing them to rotate at different speeds, especially during turns. The differential ensures stability and control during cornering.
3. Suspension and Steering
These systems ensure vehicle stability, handling, and comfort. Components include:
- Shock Absorbers: Dampen the impact of road irregularities, providing a smoother ride. Shock absorbers are essential for maintaining tire contact with the road.
- Struts: Support the vehicle’s weight and absorb shocks, integral to the suspension system. Struts combine the functions of a shock absorber and a coil spring.
- Control Arms: Connect the wheel hubs to the frame, allowing for controlled movement. Control arms play a crucial role in maintaining proper wheel alignment.
- Steering Rack and Pinion: Translate the driver’s steering input into wheel movement. This mechanism provides precise control over the vehicle’s direction.
4. Brake System
Essential for vehicle safety, the brake system allows for controlled deceleration and stopping. Key parts include:
- Brake Pedal: Initiates the braking process when pressed by the driver. The brake pedal is the primary interface for the driver to control the braking system.
- Master Cylinder: Converts pedal pressure into hydraulic force. The master cylinder distributes this force to the brake calipers or wheel cylinders.
- Brake Calipers: House the brake pads and apply pressure to the rotors to slow the vehicle. Calipers are crucial in disc brake systems for effective stopping power.
- Brake Pads and Rotors: Create friction to decelerate and stop the vehicle. Regular inspection and replacement of brake pads and rotors are vital for maintaining braking efficiency.
5. Electrical System
Modern vehicles rely heavily on electrical components for operation and comfort. Important elements include:
- Battery: Provides the electrical energy needed to start the engine and power accessories. The battery is essential for the initial ignition and supports electronic systems when the engine is off.
- Alternator: Charges the battery and powers electrical systems while the engine runs. The alternator ensures a continuous supply of electricity to the vehicle’s systems.
- Starter Motor: Turns the engine over during ignition. The starter motor initiates the engine’s operation by rotating the crankshaft.
- Fuses and Relays: Protect electrical circuits from overloads and control the operation of various components. Fuses and relays are critical for preventing electrical failures and ensuring system reliability.
6. Fuel System
This system stores and supplies fuel to the engine. Components include:
- Fuel Tank: Stores gasoline or diesel. The fuel tank is designed to safely contain the vehicle’s fuel supply.
- Fuel Pump: Delivers fuel from the tank to the engine. The fuel pump ensures a consistent flow of fuel under the required pressure.
- Fuel Injectors: Spray fuel into the engine’s combustion chambers for mixing with air. Fuel injectors provide precise fuel delivery for optimal combustion efficiency.
7. Exhaust System
Responsible for directing and treating combustion gases away from the engine. Key parts include:
- Exhaust Manifold: Collects exhaust gases from the engine’s cylinders. The manifold directs these gases into the exhaust system.
- Catalytic Converter: Reduces harmful emissions by converting them into less harmful substances. The catalytic converter plays a significant role in meeting environmental regulations.
- Muffler: Dampens the noise produced by exhaust gases. The muffler ensures that the vehicle operates within acceptable noise levels.
8. Cooling System
Maintains optimal engine temperature to prevent overheating. Components include:
- Radiator: Dissipates heat from the engine coolant. The radiator is essential for regulating engine temperature.
- Water Pump: Circulates coolant throughout the engine. The water pump ensures that coolant flows efficiently to absorb and dissipate heat.
- Thermostat: Regulates coolant flow based on engine temperature. The thermostat maintains the engine within its optimal operating temperature range.
9. Body and Interior
The car’s body and interior provide structure and comfort. Key parts include:
- Chassis: The vehicle’s frame, supporting all components. The chassis provides structural integrity and impacts the vehicle’s handling characteristics.
- Doors and Windows: Provide access and visibility. Proper functioning doors and windows are essential for safety and comfort.
- Seats: Designed for occupant comfort and safety. Modern seats often include ergonomic designs and safety features like airbags.
- Dashboard: Houses instruments and controls for vehicle operation. The dashboard provides the driver with essential information and access to vehicle controls.
Keep in mind that when looking for the perfect material for car body customization, you have to consider your budget, compatibility with your ride, and the qualities of each material. Whether you’re restoring a classic or upgrading a modern vehicle, choosing the right materials can significantly affect both performance and aesthetics.
For a visual overview of car parts and their functions, you might find the following video helpful:
Conclusion
Understanding the various parts of a car and their functions is crucial for both car owners and enthusiasts. Each component, from the engine and transmission to the tires and brakes, plays a vital role in ensuring the vehicle operates safely and efficiently. Familiarizing yourself with these parts not only empowers you to better maintain your vehicle but also helps you communicate effectively with mechanics and make informed decisions about repairs and upgrades.
By appreciating how these systems work together, you can extend your car’s lifespan, improve performance, and enhance your driving experience. Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned driver, taking the time to learn about your car’s anatomy is a worthwhile investment for smooth and hassle-free journeys ahead.
Drive safe and take good care of your car!