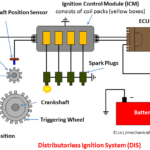
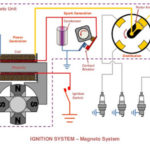
Your car’s ignition coil is an essential component in the engine’s ignition system, transforming the battery’s voltage into the energy required to create the spark that ignites the fuel-air mixture in the engine. When an ignition coil fails, it can cause several issues, affecting engine performance and fuel efficiency. Recognizing the symptoms of a bad ignition coil can help you address the problem early, avoiding more serious and costly repairs.
In this article, we’ll cover common signs of a bad ignition coil, the role it plays in your engine, and tips on diagnosing and addressing ignition coil issues.
What is an Ignition Coil, and Why Is It Important?
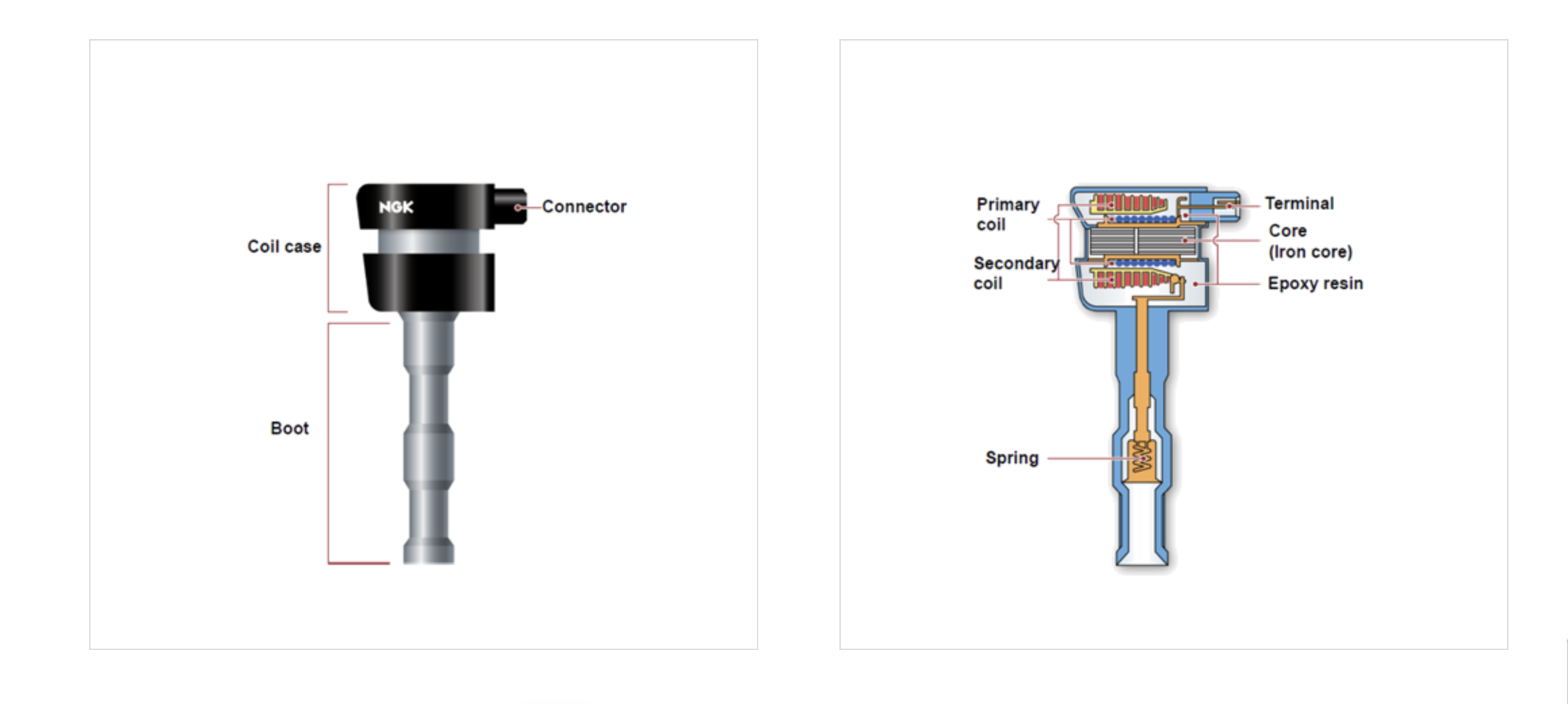
The ignition coil is a key component of the ignition system. It converts the 12 volts from the car’s battery to the thousands of volts needed to create a spark strong enough to ignite the fuel-air mixture inside the engine cylinders. Modern cars usually have one ignition coil per cylinder, allowing more control over each spark. This means that if one ignition coil fails, it can impact a specific cylinder and, consequently, the entire engine’s performance.
Common Symptoms of a Bad Ignition Coil
1. Engine Misfire
- Description: One of the most common signs of a faulty ignition coil is an engine misfire. This occurs when the fuel in the engine cylinders does not ignite properly. You may experience a rough idle, hesitation when accelerating, or even a sudden “jerking” motion as you drive.
- Why It Happens: When an ignition coil malfunctions, it fails to deliver the required spark, causing the engine to misfire. This issue often worsens under load, such as when you’re accelerating.
2. Poor Fuel Economy
- Description: You may notice you’re filling up your tank more frequently or that your miles per gallon (MPG) have dropped.
- Why It Happens: A faulty ignition coil can lead to incomplete combustion, resulting in unburned fuel passing through the exhaust system. The engine compensates by consuming more fuel to maintain power, leading to reduced fuel economy.
3. Illuminated Check Engine Light
- Description: An illuminated check engine light on your dashboard is a clear sign that something’s wrong under the hood.
- Why It Happens: A malfunctioning ignition coil often triggers the check engine light, especially in newer cars. Your car’s onboard diagnostics system (OBD-II) can store trouble codes, which can help pinpoint the issue if you use a code reader or visit a mechanic.
4. Difficulty Starting the Engine
- Description: When you turn the key or press the start button, the engine might struggle to turn over, or you may experience long cranking times.
- Why It Happens: If one or more ignition coils aren’t providing a spark, the engine may fail to start efficiently. This issue is more common in colder weather when additional energy is needed for ignition.
5. Reduced Engine Power
- Description: A sudden loss in power, sluggish acceleration, or a lack of response when pressing the accelerator are all signs of reduced engine power.
- Why It Happens: Faulty ignition coils prevent the engine from receiving the required spark, leading to a loss of power. This is especially noticeable when the engine is under heavy load or when you’re driving up an incline.
6. Rough Idle
- Description: Your car may idle roughly, meaning it shakes or vibrates noticeably when idling.
- Why It Happens: A bad ignition coil fails to ignite the fuel-air mixture consistently, causing the engine to “stumble” at idle. You may hear unusual sounds, feel vibrations, or notice inconsistent RPMs.
7. Backfiring and Exhaust Issues
- Description: Backfiring can occur when unburned fuel exits through the exhaust, creating a loud “bang” sound. You may also notice smoke or an unusual smell from the exhaust.
- Why It Happens: A failing ignition coil can cause incomplete combustion, leaving unburned fuel that exits the exhaust system. Over time, this can damage the exhaust and catalytic converter.
Causes of Ignition Coil Failure
Understanding what causes ignition coils to fail can help you prevent issues. Here are a few common reasons:
- Heat and Vibration: Constant exposure to heat and engine vibrations can degrade the ignition coil over time.
- Wear and Tear: Like all parts, ignition coils wear out. Older coils or those with high mileage are more prone to failure.
- Moisture and Oil Leakage: Water or oil leaks can cause coil failure, especially in engines with worn-out seals or gaskets.
- Electrical Surges: Voltage surges or other electrical issues in the ignition system can damage the ignition coil.
Diagnosing a Bad Ignition Coil
If you suspect a faulty ignition coil, there are a few steps you can take to confirm the diagnosis:
- OBD-II Scanner: Use an OBD-II scanner to read trouble codes from your car’s computer. Codes like P0301 to P0312 indicate misfire in specific cylinders, which can help you identify the affected coil.
- Multimeter Test: A multimeter can measure the resistance in the ignition coil. A significant deviation from the standard resistance range typically indicates a faulty coil.
- Swap Test: If you have a multi-coil setup, swap the suspected coil with one from a different cylinder and see if the misfire follows the coil. If it does, you’ve identified the bad coil.
Can You Drive with a Bad Ignition Coil?
Driving with a bad ignition coil is possible, but it’s not recommended. Misfiring and incomplete combustion can lead to damage to other components, such as the catalytic converter, and increase fuel consumption. Long-term driving with a faulty coil may result in more costly repairs.
Replacing a Bad Ignition Coil
Replacing an ignition coil isn’t overly complex, but it varies depending on your vehicle’s setup. Here are some steps if you’re considering replacing it yourself:
- Disconnect the Battery: Safety first—disconnect the battery to avoid electric shock.
- Access the Coil Pack: Locate the coil pack on the engine; you may need to remove parts like the air intake or engine cover.
- Remove the Faulty Coil: Disconnect any electrical connectors and remove the bolts securing the coil.
- Install the New Coil: Attach the new coil, reconnect the electrical connectors, and replace any parts you removed.
If you’re not comfortable doing it yourself, a mechanic can typically replace an ignition coil in under an hour.
Conclusion
A bad ignition coil can cause a range of symptoms, from engine misfires and poor fuel economy to backfiring and a rough idle. If you notice any of these symptoms, it’s essential to address the issue promptly to avoid further damage. By understanding the symptoms and diagnosing the problem, you can keep your engine running smoothly and ensure a reliable driving experience.