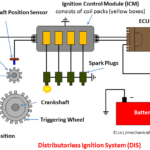
A four-stroke spark ignition engine is also known as the petrol engine and is widely used in bikes and cars as the power unit. It converts the chemical energy of fuel into mechanical energy by the piston. By knowing the working of this engine we can able to find out why our vehicle is not working properly.
The power generation process in a SI engine is divided into four parts, each part known as the piston stroke. In an engine, stroke refers to the maximum distance traveled by the piston in a single direction. The piston is free to move only in upward and downward directions. In four-stroke engine, the piston moves two times up and down and the crankshaft moves two complete revolutions to complete four piston stroke. These are intake stroke, compression stroke, expansion stroke, and exhaust stroke.

Intake Stroke:
During the intake stroke of the spark ignition engine, the piston moves down from the top end of the cylinder to the bottom end of the cylinder, and simultaneously intake valve opens. Due to the movement of piston low pressure or vacuum generates inside the cylinder. Due to this vacuum and the gravity action air-fuel mixture enter into the cylinder through the intake valve. The intake valve remains open until the piston reaches the lower end of the cylinder. After that, the intake valve closes and seals the upper end of the cylinder.

Compression Stroke:
After the piston passes the bottom end of the cylinder, it starts moving up. Both valves are closed and the cylinder is sealed. The piston moves upward. This movement of piston compresses the air fuel mixture into a small space between the top of the piston and the cylinder head. The mixture is compressed into 1/8 or less of its original volume. This compression ratio decides the power of the engine. At the end of the compression stroke, the piston is at the top end of the cylinder.

Power Stroke:
At the end of the compression stroke when the piston is at the top end of the cylinder an electric spark is generated by the spark plug. The heat of the spark ignites the compressed air-fuel mixture. The air-fuel mixture then burns rapidly and produces high temperatures up to 3300 degrees Celsius. This high temperature causes very high pressure, which pushes down on the top of the piston. The connecting rod carries this force to the crankshaft, which turns to move the vehicle. At the end of the power stroke, the piston reaches the bottom end of the cylinder.

Exhaust Stroke:
When the piston reaches the bottom end of the cylinder on the power stroke, the exhaust valve opens. At this time due to the burnt gases inside the cylinder, the pressure inside the cylinder is slightly high from atmospheric pressure. This pressure difference allows burn gases to escape through the exhaust port and the piston move through the top end of the cylinder. At the end of the exhaust, all burn gases escape and the exhaust valve closes. Now again intake valve opens and this process keeps on running until your vehicle remains in the starting position.

For a Better Understanding of how a four-stroke petrol engine works, watch the video given below: